Prospective Antiviral Effect of Ulva lactuca Aqueous Extract against COVID-19 Infection
- PMID: 38248655
- PMCID: PMC10817659
- DOI: 10.3390/md22010030
Prospective Antiviral Effect of Ulva lactuca Aqueous Extract against COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
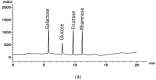
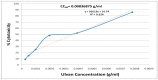
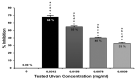
Marine algal extracts exhibit a potent inhibitory effect against several enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. The infection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has several adverse effects, including an increased mortality rate. The anti-COVID-19 agents are still limited; this issue requires exploring novel, effective anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic approaches. This study investigated the antiviral activity of an aqueous extract of Ulva lactuca, which was collected from the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. The aqueous extract of Ulva lactuca was characterized by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses. According to the HPLC analysis, the extract comprises several sugars, mostly rhamnose (32.88%). The FTIR spectra showed numerous bands related to the functional groups. EDX analysis confirmed the presence of different elements, such as oxygen (O), carbon (C), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and sodium (Na), with different concentrations. The aqueous extract of U. lactuca (0.0312 mg/mL) exhibited potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity via virucidal activity, inhibition of viral replication, and interference with viral adsorption (% inhibitions of 64%, 33.3%, and 31.1%, respectively). Consequently, ulvan could be a promising compound for preclinical study in the drug development process to combat SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Egypt; Ulva lactuca; anti-SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; ulvan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Domínguez H. Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals. Elsevier Science; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. Algae as a Source of Biologically Active Ingredients for the Formulation of Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals; pp. 1–19. - DOI
-
- Moreira A., Cruz S., Marques R., Cartaxana P. The Underexplored Potential of Green Macroalgae in Aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2022;14:5–26. doi: 10.1111/raq.12580. - DOI
-
- Gheda S., El-Sheekh M.M., Abou-Zeid A. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Polysaccharide Extracted from the Red Alga Jania rubens Against Breast and Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018;11:583–589. doi: 10.4103/1995-7645.244523. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

