Antioxidant, Antibacterial Properties of Novel Peptide CP by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chromis notata By-Products and Its Efficacy on Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 38248669
- PMCID: PMC10817315
- DOI: 10.3390/md22010044
Antioxidant, Antibacterial Properties of Novel Peptide CP by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chromis notata By-Products and Its Efficacy on Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
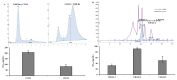
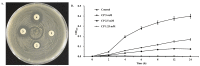
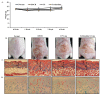
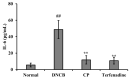
This study investigated the antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-atopic dermatitis (AD) effects of a novel peptide (CP) derived from a Chromis notata by-product hydrolysate. Alcalase, Flavourzyme, Neutrase, and Protamex enzymes were used to hydrolyze the C. notata by-product protein, and the 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activity was measured. Alcalase hydrolysate exhibited the highest ABTS radical-scavenging activity, leading to the selection of Alcalase for further purification. The CHAO-1-I fraction, with the highest ABTS activity, was isolated and further purified, resulting in the identification of the peptide CP with the amino acid sequence Ala-Gln-Val-Met-Lys-Leu-Pro-His-Arg-Met-Gln-His-Ser-Gln-Ser. CP demonstrated antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, inhibiting its growth. In a 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-induced AD-like skin model in mice, CP significantly alleviated skin lesions, reduced epidermal and dermal thickness, and inhibited mast cell infiltration. Moreover, CP suppressed the elevated levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the plasma of DNCB-induced mice. These findings highlight the potential of CP as a therapeutic agent for AD and suggest a novel application of this C. notata by-product in the fish processing industry.
Keywords: Chromis notata; antimicrobial activity; antioxidant peptide; atopic dermatitis; by-product hydrolysate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antioxidative and Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of Peptides Derived from Hydrolyzed Sebastes schlegelii Tail By-Products.Mar Drugs. 2024 Oct 19;22(10):479. doi: 10.3390/md22100479. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452887 Free PMC article.
-
Purification, Identification, Activity Evaluation, and Stability of Antioxidant Peptides from Alcalase Hydrolysate of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Proteins.Mar Drugs. 2021 Jun 17;19(6):347. doi: 10.3390/md19060347. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34204535 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, Identification, and Activity Evaluation of Eight Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Hairtail (Trichiurus japonicas) Muscle.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jan 2;17(1):23. doi: 10.3390/md17010023. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30609694 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of antioxidative corn protein hydrolysates, purification and evaluation of three novel corn antioxidant peptides.Food Chem. 2016 Aug 1;204:427-436. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.119. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26988521
-
Comparative study on structural, biological and functional activities of hydrolysates from Adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) and mung bean (Vigna radiata) protein concentrates using Alcalase and Flavourzyme.Food Res Int. 2022 Nov;161:111797. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111797. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36192943
Cited by
-
Antioxidative and Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of Peptides Derived from Hydrolyzed Sebastes schlegelii Tail By-Products.Mar Drugs. 2024 Oct 19;22(10):479. doi: 10.3390/md22100479. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452887 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Skin-Whitening Efficacy of a Novel Decapeptide (DP, KGYSSYICDK) Derived from Fish By-Products.Mar Drugs. 2024 Aug 20;22(8):374. doi: 10.3390/md22080374. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakatsuji T., Chen T.H., Narala S., Chun K.A., Two A.M., Yun T., Shafiq F., Kotol P.F., Bouslimani A., Melnik A.V., et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017;9:4680. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aah4680. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

