Preschool Children with Hearing Loss: Social Communication and Parenting Stress
- PMID: 38248749
- PMCID: PMC10821039
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14010047
Preschool Children with Hearing Loss: Social Communication and Parenting Stress
Abstract
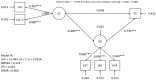
Studies on parenting stress (PS) in parents of children with hearing loss (HL) have found relationships between child behavior, language skills and parenting stress. The role of early social communication skills has not been researched before. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to investigate the relationship between child behavior, social communication and PS. The study was performed in a subgroup of a total population sample from the AChild (Austrian Children with Hearing Impairment-Longitudinal Databank) study. Preschool children (n = 81) with all degrees of HL and average cognitive functioning and their families were included, and the Parenting Stress Index (PSI) was used. Through factor component analysis, compound scores for externalizing/internalizing problem behavior and hyperactivity were analyzed. Although mean PS was not elevated, the proportion of those with elevated scores was higher compared with the norm population. There was a strong correlation between child behavior problems and PS (strongest correlation: externalizing problem behavior r = 0.643; p < 0.001). All three problem behaviors accounted for 49.7% of the variance in PS. An indirect effect of social communication on PS was almost completely mediated by problem behavior (especially hyperactivity). The importance of social communication development with respect to problem behavior and PS is highlighted.
Keywords: child; deaf and hard of hearing; parenting stress; parent–child interaction; problem behavior; social communication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early identification: Language skills and social functioning in deaf and hard of hearing preschool children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Dec;79(12):2221-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26514930
-
Associations Between Parenting Stress, Language Comprehension, and Inhibitory Control in Children With Hearing Loss.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2020 Jan 15;63(1):321-333. doi: 10.1044/2019_JSLHR-19-00230. Print 2020 Jan 22. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2020. PMID: 31940261 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting Stress among Parents of Deaf and Hearing Children: Associations with Language Delays and Behavior Problems.Parent Sci Pract. 2010 Apr 1;10(2):136-155. doi: 10.1080/15295190903212851. Parent Sci Pract. 2010. PMID: 20607098 Free PMC article.
-
[Hearing impairment and psychopathological disorders in children and adolescents. Review of the recent literature].Encephale. 2003 Jul-Aug;29(4 Pt 1):329-37. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14615703 Review. French.
-
Responsive parenting intervention after identification of hearing loss by Universal Newborn Hearing Screening: the concept of the Muenster Parental Programme.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Dec;77(12):2030-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 24182601 Review.
References
-
- Selye H. The Stress of Life. Revised ed. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY, USA: 1984.
-
- Lazarus R.S. Stress and Emotion: A New Synthesis. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2006.
-
- Abidin R.R. Parenting Stress Index (PSI) Pediatric Psychology Press; Charlottesville, VA, USA: 1990.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources