Perspectives on Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment
- PMID: 38248752
- PMCID: PMC10817460
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14010051
Perspectives on Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment
Abstract
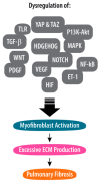
Pulmonary fibrosis, a critical outcome of chronic inflammatory diseases, has gained prominence in the context of post-coronavirus (post-COVID-19) complications. This review delves into the multifaceted landscape of post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis, elucidating the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and highlighting promising therapeutic avenues. Examining the aftermath of severe acute respiratory syndrome-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, the review reveals key signaling pathways implicated in the fibrotic cascade. Drawing parallels with previous coronavirus outbreaks enhances our understanding of the distinctive features of post-COVID-19 fibrosis. Antifibrotic drugs, like pirfenidone and nintedanib, take center stage; their mechanisms of action and potential applications in post-COVID-19 cases are thoroughly explored. Beyond the established treatments, this review investigates emerging therapeutic modalities, including anti-interleukin agents, immunosuppressants, and experimental compounds, like buloxybutide, saracatinib, sirolimus, and resveratrol. Emphasizing the critical importance of early intervention, this review highlights the dynamic nature of post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis research. In conclusion, the synthesis of current knowledge offers a foundation for advancing our approaches to the prevention and treatment of these consequential sequelae of COVID-19.
Keywords: antifibrotic; fibrosis; nintedanib; pirfenidone; post-COVID-19; pulmonary; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [(accessed on 12 December 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19.
-
- World Health Organization Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. [(accessed on 13 December 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Horberg M.A., Watson E., Bhatia M., Jefferson C., Certa J.M., Kim S., Fathi L., Althoff K.N., Williams C., Moore R. Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 with clinical condition definitions and comparison in a matched cohort. Nat. Commun. 2022;131:5822. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33573-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Post-COVID-19 Condition. [(accessed on 18 November 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-dis....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

