Critical Factors in Sample Collection and Preparation for Clinical Metabolomics of Underexplored Biological Specimens
- PMID: 38248839
- PMCID: PMC10819689
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo14010036
Critical Factors in Sample Collection and Preparation for Clinical Metabolomics of Underexplored Biological Specimens
Abstract
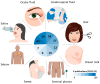
This review article compiles critical pre-analytical factors for sample collection and extraction of eight uncommon or underexplored biological specimens (human breast milk, ocular fluids, sebum, seminal plasma, sweat, hair, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid) under the perspective of clinical metabolomics. These samples are interesting for metabolomics studies as they reflect the status of living organisms and can be applied for diagnostic purposes and biomarker discovery. Pre-collection and collection procedures are critical, requiring protocols to be standardized to avoid contamination and bias. Such procedures must consider cleaning the collection area, sample stimulation, diet, and food and drug intake, among other factors that impact the lack of homogeneity of the sample group. Precipitation of proteins and removal of salts and cell debris are the most used sample preparation procedures. This review intends to provide a global view of the practical aspects that most impact results, serving as a starting point for the designing of metabolomic experiments.
Keywords: biological specimens; biomarkers; mass spectrometry; metabolite extraction; metabolomics; non-invasive collection; pre-analytical factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From bedside to bench-practical considerations to avoid pre-analytical pitfalls and assess sample quality for high-resolution metabolomics and lipidomics analyses of body fluids.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Sep;413(22):5567-5585. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03450-0. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34159398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of blood sample handling and pre-processing for metabolomics studies.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(18):2232-2241. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700086. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28543881 Review.
-
Metabolic profiling of body fluids and multivariate data analysis.MethodsX. 2017 Feb 20;4:95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2017.02.004. eCollection 2017. MethodsX. 2017. PMID: 28275554 Free PMC article.
-
Bias caused by incomplete metabolite extraction and matrix effect: Evaluation of critical factors for plasma sample preparation prior to metabolomics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022 Sep 20;219:114930. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114930. Epub 2022 Jul 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022. PMID: 35839581
-
Interpreting γ-hydroxybutyrate concentrations for clinical and forensic purposes.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019 Mar;57(3):149-163. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2018.1519194. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 30307336 Review.
References
-
- Kirwan J.A., Brennan L., Broadhurst D., Fiehn O., Cascante M., Dunn W.B., Schmidt M.A., Velagapudi V. Preanalytical Processing and Biobanking Procedures of Biological Samples for Metabolomics Research: A White Paper, Community Perspective (for “Precision Medicine and Pharmacometabolomics Task Group”—The Metabolomics Society Initiative) Clin. Chem. 2018;64:1158–1182. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2018.287045. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources