Myocardial Calcium Handling in Type 2 Diabetes: A Novel Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 38248882
- PMCID: PMC10817027
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd11010012
Myocardial Calcium Handling in Type 2 Diabetes: A Novel Therapeutic Target
Abstract
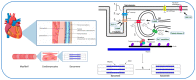
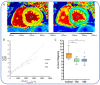
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a multisystem disease with rapidly increasing global prevalence. Heart failure has emerged as a major complication of T2D. Dysregulated myocardial calcium handling is evident in the failing heart and this may be a key driver of cardiomyopathy in T2D, but until recently this has only been demonstrated in animal models. In this review, we describe the physiological concepts behind calcium handling within the cardiomyocyte and the application of novel imaging techniques for the quantification of myocardial calcium uptake. We take an in-depth look at the evidence for the impairment of calcium handling in T2D using pre-clinical models as well as in vivo studies, following which we discuss potential novel therapeutic approaches targeting dysregulated myocardial calcium handling in T2D.
Keywords: calcium handling; diabetes; manganese-enhanced MRI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Mar 15;13:20420188221083530. doi: 10.1177/20420188221083530. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35308180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene therapy targeting cardiac phosphoinositide 3-kinase (p110α) attenuates cardiac remodeling in type 2 diabetes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):H840-H852. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00632.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32142359
-
Cardiomyocyte calcium handling in health and disease: Insights from in vitro and in silico studies.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Nov;157:54-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Mar 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32188566
-
Indirectly probing Ca(2+) handling alterations following myocardial infarction in a murine model using T(1)-mapping manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2011 Jan;65(1):239-49. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22597. Magn Reson Med. 2011. PMID: 20872864
-
Diabetes-related cardiomyopathy: The sweet story of glucose overload from epidemiology to cellular pathways.Diabetes Metab. 2019 Jun;45(3):238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Diabetes Metab. 2019. PMID: 30078623 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Basis of Cardiomyopathies in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 29;25(15):8280. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158280. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koudstaal S., Pujades-Rodriguez M., Denaxas S., Gho J., Shah A.D., Yu N., Patel R.S., Gale C.P., Hoes A.W., Cleland J.G., et al. Prognostic burden of heart failure recorded in primary care, acute hospital admissions, or both: A population-based linked electronic health record cohort study in 2.1 million people. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017;19:1119–1127. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.709. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rawshani A., Rawshani A., Franzén S., Sattar N., Eliasson B., Svensson A.-M., Zethelius B., Miftaraj M., McGuire D.K., Rosengren A., et al. Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;379:633–644. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800256. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

