Outcomes after Perioperative Transient Ischemic Attack Following Cardiac Surgery
- PMID: 38248897
- PMCID: PMC10816235
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd11010027
Outcomes after Perioperative Transient Ischemic Attack Following Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
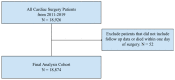
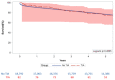
Perioperative transient ischemic attacks (PTIAs) are associated with significantly increased rates of postoperative complications such as low cardiac output, atrial fibrillation, and significantly higher mortality in cardiac procedures. The current literature on PTIAs is sparse and understudied. Therefore, we aim to understand the effects of PTIA on hospital utilization, readmission, and morbidity. Using data on all the cardiac procedures at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center from 2011 to 2019, fine and gray analysis was performed to identify whether PTIAs and covariables correlate with increased hospital utilization, stroke, all-cause readmission, Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE), MI, and all-cause mortality. Logistic regression for longer hospitalization showed that PTIA (HR: 2.199 [95% CI: 1.416-3.416] increased utilization rates. Fine and gray modeling indicated that PTIA (HR: 1.444 [95% CI: 1.096-1.902], p < 0.01) increased the rates of follow-up all-cause readmission. However, PTIA (HR: 1.643 [95% CI: 0.913-2.956] was not statistically significant for stroke readmission modeling. Multivariate modeling for MACCE events within 30 days of surgery (HR: 0.524 [95% CI: 0.171-1.605], p > 0.25) and anytime during the follow-up period (HR: 1.116 [95% CI: 0.825-1.509], p > 0.45) showed no significant correlation with PTIA. As a result of PTIA's significant burden on the healthcare system due to increased utilization, it is critical to better define and recognize PTIA for timely management to improve perioperative outcomes.
Keywords: cardiac surgery; perioperative transient ischemic attack; transient ischemic attack.
Conflict of interest statement
I.B.S. reports research and grant support from Abbott, Artivion, AtriCure, Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, and Terumo Aortic. R.G.N. reports consulting fees for advisory roles with Anaconda, Biogen, CERENOVUS, Genentech, Philips, Hybernia, Imperative Care, Medtronic, Phenox, Philips, Prolong Pharmaceuticals, Stryker Neurovascular, Shanghai Wallaby, and Synchron, and stock options for advisory roles with Astrocyte, Brainomix, Cerebrotech, Ceretrieve, Corindus Vascular Robotics, Vesalio, Viz.ai, RapidPulse, and Perfuze. R.G.N. is one of the principal investigators of the “Endovascular Therapy for Low NIHSS Ischemic Strokes (ENDOLOW)” trial. R.G.N. is the principal investigator of the “Combined Thrombectomy for Distal MediUm Vessel Occlusion StroKe (DUSK)” trial. R.G.N. is an investor in Viz.ai, Perfuze, Cerebrotech, Reist/Q’Apel Medical, Truvic, Vastrax, and Viseon.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient ischemic attack, protracted transient ischemic attack, and completed stroke.Eur Neurol. 1983;22 Suppl 1:68-73. doi: 10.1159/000115652. Eur Neurol. 1983. PMID: 6884405
-
Incidence and prognostic factors related to major adverse cerebrovascular events in patients with complex aortic diseases treated by the chimney technique.J Vasc Surg. 2018 May;67(5):1372-1379. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.08.079. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 29103932
-
Prior stroke and transient ischemic attack as risk factors for subsequent stroke in atrial fibrillation patients: A report from the GARFIELD-AF registry.Int J Stroke. 2020 Apr;15(3):308-317. doi: 10.1177/1747493019891516. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Int J Stroke. 2020. PMID: 31847794 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of percutaneous Watchman 2.5 device versus Amplatzer Amulet for left atrial appendage closure in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and study-level meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 14;19(2):e0295804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295804. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38354181 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative beta-blockers for preventing surgery-related mortality and morbidity in adults undergoing cardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 23;9(9):CD013435. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013435. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31544227 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and operative risk of large vessel occlusion and stroke during cardiac surgery.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Nov;33(11):107958. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107958. Epub 2024 Aug 17. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39159904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engelman D.T., Cohn L.H., Rizzo R.J. Incidence and predictors of tias and strokes following coronary artery bypass grafting: Report and collective review. Heart Surg. Forum. 1999;2:242–245. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez F.G., Falcoz P.E., Kozower B.D., Salati M., Wright C.D., Brunelli A. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Surgery Databases: Joint Standardization of Variable Definitions and Terminology. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015;99:368–376. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.05.104. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials