Measurement Invariance of the WISC-V across a Clinical Sample of Children and Adolescents with ADHD and a Matched Control Group
- PMID: 38248904
- PMCID: PMC10817318
- DOI: 10.3390/jintelligence12010006
Measurement Invariance of the WISC-V across a Clinical Sample of Children and Adolescents with ADHD and a Matched Control Group
Abstract
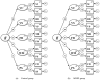
Measurement invariance of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, Fifth Edition (WISC-V) 10-primary subtest battery was analyzed across a group of children and adolescents with ADHD (n = 91) and a control group (n = 91) matched by sex, age, migration background, and parental education or type of school. First, confirmatory factor analyses (CFAs) were performed to establish the model fit for the WISC-V second-order five-factor model in each group. A sufficiently good fit of the model was found for the data in both groups. Subsequently, multigroup confirmatory factor analyses (MGCFAs) were conducted to test for measurement invariance across the ADHD and control group. Results of these analyses indicated configural and metric invariance but did not support full scalar invariance. However, after relaxing equality constraints on the Vocabulary (VC), Digit Span (DS), Coding (CD), Symbol Search (SS), and Picture Span (PS) subtest intercepts as well as on the intercepts of the first-order factors Working Memory (WM) and Processing Speed (PS), partial scalar invariance could be obtained. Furthermore, model-based reliability coefficients indicated that the WISC-V provides a more precise measurement of general intelligence (e.g., represented by the Full-Scale IQ, FSIQ) than it does for cognitive subdomains (e.g., represented by the WISC-V indexes). Group comparisons revealed that the ADHD group scored significantly lower than the control group on four primary subtests, thus achieving significantly lower scores on the corresponding primary indexes and the FSIQ. Given that measurement invariance across the ADHD and the control group could not be fully confirmed for the German WISC-V, clinical interpretations based on the WISC-V primary indexes are limited and should only be made with great caution regarding the cognitive profiles of children and adolescents with ADHD.
Keywords: ADHD; Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children; clinical sample; fifth edition; measurement invariance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Validity of the WISC-V in Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Factor Structure and Measurement Invariance.J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2021 Sep-Oct;50(5):669-681. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2020.1846543. Epub 2021 Jan 15. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33448884
-
Measurement Invariance Across Gender on the Second-Order Five-Factor Model of the German Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fifth Edition.Assessment. 2020 Dec;27(8):1836-1852. doi: 10.1177/1073191119847762. Epub 2019 May 8. Assessment. 2020. PMID: 31067991
-
Construct validity of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale For Children - Fifth UK Edition: Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses of the 16 primary and secondary subtests.Br J Educ Psychol. 2019 Jun;89(2):195-224. doi: 10.1111/bjep.12230. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Br J Educ Psychol. 2019. PMID: 29869412
-
A meta-analysis on verbal working memory in children and adolescents with ADHD.Clin Neuropsychol. 2020 Jul;34(5):873-898. doi: 10.1080/13854046.2019.1604998. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Clin Neuropsychol. 2020. PMID: 31007130 Review.
-
Cognitive Profile in Autism and ADHD: A Meta-Analysis of Performance on the WAIS-IV and WISC-V.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2024 May 21;39(4):498-515. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acad073. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2024. PMID: 37779387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Intelligence Structures of School-Age Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in China.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2024 Dec 28;20:2651-2661. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S489365. eCollection 2024. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2024. PMID: 39748915 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the factor structure of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) in adults with congenital heart disease.Clin Neuropsychol. 2024 Dec 31:1-12. doi: 10.1080/13854046.2024.2442424. Online ahead of print. Clin Neuropsychol. 2024. PMID: 39741381
-
Preliminary results of the EPIDIA4Kids study on brain function in children: multidimensional ADHD-related symptomatology screening using multimodality biometry.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Mar 17;16:1466107. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1466107. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40165864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association, editor. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2013.
-
- Arbuckle J. L. AMOS. IBM SPSS; Chicago: 2022. version 29.0.
-
- Assesmany Amy, McIntosh David E., LeAdelle Phelps, Rizza Mary G. Discriminant Validity of the WISC-III with Children Classified with ADHD. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment. 2001;19:137–47. doi: 10.1177/073428290101900203. - DOI
-
- Becker Angelika, Daseking Monika, Koerner Julia Kerner auch. Cognitive Profiles in the WISC-V of Children with ADHD and Specific Learning Disorders. Sustainability. 2021;13:9948. doi: 10.3390/su13179948. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

