Identification and Characterization of a Predominant Hydrophobin in the Edible Mushroom Grifola frondosa
- PMID: 38248935
- PMCID: PMC10820438
- DOI: 10.3390/jof10010025
Identification and Characterization of a Predominant Hydrophobin in the Edible Mushroom Grifola frondosa
Abstract
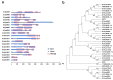
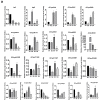
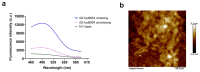
Hydrophobins (HFBs) are a group of small, secreted amphipathic proteins of fungi with multiple physiological functions and potential commercial applications. In this study, HFB genes of the edible mushroom, Grifola frondosa, were systematically identified and characterized, and their transcriptional profiles during fungal development were determined. In total, 19 typical class I HFB genes were discovered and bioinformatically analyzed. Gene expression profile examination showed that Gf.hyd9954 was particularly highly upregulated during primordia formation, suggesting its major role as the predominant HFB in the lifecycle of G. frondosa. The wettability alteration profile and the surface modification ability of recombinant rGf.hyd9954 were greater than for the Grifola HFB HGFII-his. rGf.hyd9954 was also demonstrated to form the typical class I HFB characteristic-rodlet bundles. In addition, rGf.hyd9954 was shown to possess nanoparticle characteristics and emulsification activities. This research sheds light on the regulation of fungal development and its association with the expression of HFB genes.
Keywords: fungal development; hydrophobins; life cycle; maitake; transcription levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel hydrophobin encoded by hgfII from Grifola frondosa exhibiting excellent self-assembly ability.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 9;13:990231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.990231. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160239 Free PMC article.
-
The functional role of Cys3-Cys4 loop in hydrophobin HGFI.Amino Acids. 2014 Nov;46(11):2615-25. doi: 10.1007/s00726-014-1805-0. Epub 2014 Sep 21. Amino Acids. 2014. PMID: 25240738
-
Protein HGFI from the edible mushroom Grifola frondosa is a novel 8 kDa class I hydrophobin that forms rodlets in compressed monolayers.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Jun;154(Pt 6):1677-1685. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/015263-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18524922
-
Bioactive Ingredients and Medicinal Values of Grifola frondosa (Maitake).Foods. 2021 Jan 5;10(1):95. doi: 10.3390/foods10010095. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33466429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polysaccharides in Grifola frondosa mushroom and their health promoting properties: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Aug;101:910-921. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.177. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28366857 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-mediated stabilization of amphotericin B increases its efficacy against diverse fungal pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):e0068625. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00686-25. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40243314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wessels J.G.H. Fungal hydrophobins: Proteins that function at an interface. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1:9–15. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(96)80017-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

