The Diverse Mycorrizal Morphology of Rhododendron dauricum, the Fungal Communities Structure and Dynamics from the Mycorrhizosphere
- PMID: 38248974
- PMCID: PMC10817234
- DOI: 10.3390/jof10010065
The Diverse Mycorrizal Morphology of Rhododendron dauricum, the Fungal Communities Structure and Dynamics from the Mycorrhizosphere
Abstract
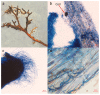
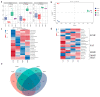
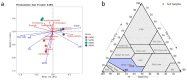
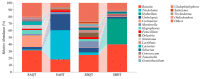
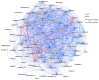
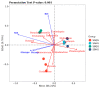
It is generally believed that mycorrhiza is a microecosystem composed of mycorrhizal fungi, host plants and other microscopic organisms. The mycorrhiza of Rhododendron dauricum is more complex and the diverse morphology of our investigated results displays both typical ericoid mycorrhizal characteristics and ectomycorrhizal traits. The characteristics of ectendoomycorrhiza, where mycelial invade from the outside into the root cells, have also been observed. In order to further clarify the mycorrhizal fungi members and other fungal communities of R. dauricum mycorrhiza, and explore the effects of vegetation and soil biological factors on their community structure, we selected two woodlands in the northeast of China as samples-one is a mixed forest of R. dauricum and Quercus mongolica, and the other a mixed forest of R. dauricum, Q. mongolica, and Pinus densiflor. The sampling time was during the local growing season, from June to September. High-throughput sequencing yielded a total of 3020 fungal amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), which were based on sequencing of the internal transcribed spacer ribosomal RNA (ITS rRNA) via the Illumina NovaSeq platform. In the different habitats of R. dauricum, there are differences in the diversity of fungi obtained from mycorrhizal niches, and specifically the mycorrhizal fungal community structure in the complex vegetation of mixed forests, where R. dauricum is found, exhibits greater stability, with relatively minor changes over time. Soil fungi are identified as the primary source of fungi within the mycorrhizal niche, and the abundance of mycorrhizal fungi from mycorrhizal niches in R. dauricum is significantly influenced by soil pH, organic matter, and available nitrogen. The relationship between soil fungi and mycorrhizal fungi from mycorrhizal niches is simultaneously found to be intricate, while the genus Hydnellum emerges as a central genus among mycorrhizal fungi from mycorrhizal niches. However, there is currently a substantial gap in the foundational research of this genus, including the fact that mycorrhizal fungi from mycorrhizal niches have, compared to fungi present in the soil, proven to be more sensitive to changes in soil moisture.
Keywords: ecological niches; ericoid mycorrhiza; forest type; fungi community; mycorrhiza.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Taura F., Iijima M., Yamanaka E., Takahashi H., Kenmoku H., Saeki H., Morimoto S., Asakawa Y., Kurosaki F., Morita H. A Novel Class of Plant Type III Polyketide Synthase Involved in Orsellinic Acid Biosynthesis from Rhododendron dauricum. Front. Plant Sci. 2016;7:1452. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01452. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

