Effect of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria on Antioxidant Status, Acetolactate Synthase Activity, and Growth of Common Wheat and Canola Exposed to Metsulfuron-Methyl
- PMID: 38249102
- PMCID: PMC10801594
- DOI: 10.3390/jox14010005
Effect of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria on Antioxidant Status, Acetolactate Synthase Activity, and Growth of Common Wheat and Canola Exposed to Metsulfuron-Methyl
Abstract
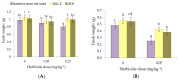
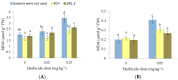
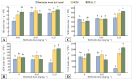
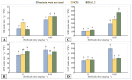
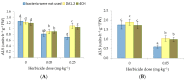
Metsulfuron-methyl, a widely used herbicide, could cause damage to the sensitive plants in crop-rotation systems at extremely low levels in the soil. The potential of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) for enhancing the resistance of plants against herbicide stress has been discovered recently. Therefore, it is poorly understood how physiological processes occur in plants, while PGPB reduce the phytotoxicity of herbicides for agricultural crops. In greenhouse studies, the effect of strains Pseudomonas protegens DA1.2 and Pseudomonas chlororaphis 4CH on oxidative damage, acetolactate synthase (ALS), enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants in canola (Brassica napus L.), and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) were investigated under two levels (0.05 and 0.25 mg∙kg-1) of metsulfuron-methyl using spectrophotometric assays. The inoculation of herbicide-exposed wheat with bacteria significantly increased the shoots fresh weight (24-28%), amount of glutathione GSH (60-73%), and flavonoids (5-14%), as well as activity of ascorbate peroxidase (129-140%), superoxide dismutase SOD (35-49%), and ALS (50-57%). Bacterial treatment stimulated the activity of SOD (37-94%), ALS (65-73%), glutathione reductase (19-20%), and the accumulation of GSH (61-261%), flavonoids (17-22%), and shoots weight (27-33%) in herbicide-exposed canola. Simultaneous inoculation prevented lipid peroxidation induced by metsulfuron-methyl in sensitive plants. Based on the findings, it is possible that the protective role of bacterial strains against metsulfuron-metil is linked to antioxidant system activation.
Keywords: acetolactate synthase; antioxidant enzymes; antioxidants; bacteria; biostimulant; herbicide; metsulfuron-methyl; safeners.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Influence of Plant Growth-Stimulating Bacteria on the Glutathione-S-Transferase Activity and the Toxic Effect of the Herbicide Metsulfuron-Methyl in Wheat and Canola Plants.Toxics. 2024 Dec 5;12(12):886. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120886. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771101 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Mechanism to Metsulfuron-Methyl in Polypogon fugax.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 28;10(7):1309. doi: 10.3390/plants10071309. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203227 Free PMC article.
-
RESISTANCE TO ALS-INHIBITING HERBICIDES IN WEED POPULATIONS FROM BELGIAN WHEAT FIELDS.Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2015;80(2):251-9. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 27145589
-
Biological responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum) plants to the herbicide simetryne in soils.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016 May;127:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016. PMID: 26803524
-
Exogenous addition of silicon alleviates metsulfuron methyl induced stress in wheat seedlings.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Oct;167:705-712. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.031. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34500195
Cited by
-
The Influence of Plant Growth-Stimulating Bacteria on the Glutathione-S-Transferase Activity and the Toxic Effect of the Herbicide Metsulfuron-Methyl in Wheat and Canola Plants.Toxics. 2024 Dec 5;12(12):886. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120886. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771101 Free PMC article.
-
PGPB-driven bioenrichment and metabolic modulation of Salicornia europaea under marine Aquaponic conditions.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 7;41(4):124. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04335-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40189660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaur T., Brar L.S. Residual effect of wheat applied sulfonylurea herbicides on succeeding crops as affected by soil pH. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2014;46:241–243.
-
- Mehdizadeh M., Alebrahim M.T., Roushani M., Streibig J.G. Evaluation of four different crops’ sensitivity to sulfosulfuron and tribenuron methyl soil residues. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2016;66:706–713. doi: 10.1080/09064710.2016.1212919. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

