Harnessing the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Review on Advancing Therapeutic Strategies for Rheumatic Diseases
- PMID: 38249228
- PMCID: PMC10800157
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50964
Harnessing the Microbiome: A Comprehensive Review on Advancing Therapeutic Strategies for Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
Rheumatic diseases are a group of disorders that affect the joints, muscles, and bones. These diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriatic arthritis, can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, leading to reduced mobility and disability. Recent studies have identified the microbiome, the diverse community of microorganisms that live in and on the human body, as a potential factor in the development and progression of rheumatic diseases. Harnessing the microbiome offers a promising new avenue for developing therapeutic strategies for these debilitating conditions. There is growing interest in the role of oral and gut microbiomes in the management of rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disease. Microbial metabolites have immunomodulatory properties that could be exploited for rheumatic disorders. A wide range of microorganisms are present in the oral cavity and are found to be vulnerable to the effects of the environment. The physiology and ecology of the microbiota become intimately connected with those of the host, and they critically influence the promotion of health or progression toward disease. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on oral and gut microbiome and its potential future role in the management of rheumatic diseases. This article will also discuss newer treatment strategies such as bioinformatic analyses and fecal transplantation.
Keywords: autoimmune connective tissue disease; autoimmune rheumatic diseases; future therapeutic strategies; human microbiome; intestinal microbiome.
Copyright © 2023, Bhattacharjee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
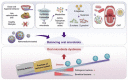
Figures

References
-
- The microbiome: a revolution in treatment for rheumatic diseases? Rosenbaum JT, Asquith MJ. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016;18:62. - PubMed
-
- The metabolic role of the gut microbiota in health and rheumatic disease: mechanisms and interventions. Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Abramson SB, Scher JU. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:446–455. - PubMed
-
- Microbiota and metabolites in rheumatic diseases. Tong Y, Marion T, Schett G, Luo Y, Liu Y. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19:102530. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
