Clinicopathological Correlation of Polyomavirus Nephropathy in Renal Allograft Recipients According to the Banff 2018 Classification
- PMID: 38249254
- PMCID: PMC10799693
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50910
Clinicopathological Correlation of Polyomavirus Nephropathy in Renal Allograft Recipients According to the Banff 2018 Classification
Abstract
Background: Polyomavirus nephropathy (PVN) is a rare kidney disease caused by the BK virus, a strain of polyomavirus. The disease primarily affects transplant recipients, which is related to intensive immunosuppression protocol and can lead to kidney allograft failure.
Objectives: The objective of this study is to analyze histopathological features of PVN using the Banff 2018 PVN classification and to determine clinical features and outcomes of patients with PVN in each histologic class.
Materials and methods: The study included 44 patients who had been diagnosed with PVN by renal allograft biopsy in a large tertiary care hospital in Thailand from January 2011 to January 2020. The kidney biopsy slides were reviewed for Banff 2018 PVN classification and other histologic features. Patient demographic information, clinical data, and laboratory results were retrospectively collected.
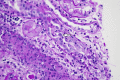
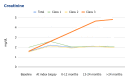
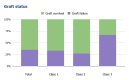
Results: Nine (20.45%), 27 (61.36%), and eight (18.18%) cases of PVN were Class I, Class II, and Class III, respectively. The time from transplant to PVN diagnosis for Classes I, II, and III was four, 19, and 33.5 months, respectively. Class III had the worst clinical outcomes in terms of deterioration of allograft function, the lowest rate of resolution, and the highest rate of graft failure.
Conclusions: PVN classification provides prognostic information in renal allograft biopsy. Our study confirmed the validity of the three-tier histologic PVN classification put forward by the Banff Working Group in 2018.
Keywords: histologic classification; polyomavirus nephropathy; renal pathology; transplant infection; transplant pathology.
Copyright © 2023, Junyangdikul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Revisit of Polyomavirus Nephropathy Grading in Renal Allograft Recipients According to the Banff 2019 Working Group Classification: A Study From a Large Transplant Center in South India.Cureus. 2022 Feb 19;14(2):e22377. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22377. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35321062 Free PMC article.
-
The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: A multicenter validation study in the modern era.Am J Transplant. 2021 Feb;21(2):669-680. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16189. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 32654412 Free PMC article.
-
The Banff Working Group Classification of Definitive Polyomavirus Nephropathy: Morphologic Definitions and Clinical Correlations.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Feb;29(2):680-693. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017050477. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29279304 Free PMC article.
-
Polyomavirus nephropathy - recent pathological diagnostic problems and the report from the 2011 Banff meeting.Clin Transplant. 2012 Jul;26 Suppl 24:9-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2012.01648.x. Clin Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22747469 Review.
-
Basic and clinical research in polyomavirus nephropathy.Exp Clin Transplant. 2004 Jun;2(1):162-73. Exp Clin Transplant. 2004. PMID: 15859923 Review.
References
-
- Population-based study of antibody to the human polyomaviruses BKV and JCV and the simian polyomavirus SV40. Knowles WA, Pipkin P, Andrews N, Vyse A, Minor P, Brown DW, Miller E. J Med Virol. 2003;71:115–123. - PubMed
-
- The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: a multicenter validation study in the modern era. Nickeleit V, Singh HK, Dadhania D, et al. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.16189. Am J Transplant. 2021;21:669–680. - PMC - PubMed
-
- An OPTN analysis of national registry data on treatment of BK virus allograft nephropathy in the United States. Dharnidharka VR, Cherikh WS, Abbott KC. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31819cc383. Transplantation. 2009;87:1019–1026. - PubMed
-
- BK virus infection: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Sawinski D, Goral S. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Progress in pathological diagnosis after kidney transplantation: current trend and future perspective. Masutani K. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV22005. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2023;30:720–732. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
