Regulation and functions of the NLRP3 inflammasome in RNA virus infection
- PMID: 38249297
- PMCID: PMC10796458
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1309128
Regulation and functions of the NLRP3 inflammasome in RNA virus infection
Abstract
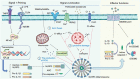
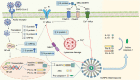
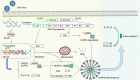
Virus infection is one of the greatest threats to human life and health. In response to viral infection, the host's innate immune system triggers an antiviral immune response mostly mediated by inflammatory processes. Among the many pathways involved, the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome has received wide attention in the context of viral infection. The NLRP3 inflammasome is an intracellular sensor composed of three components, including the innate immune receptor NLRP3, adaptor apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC), and the cysteine protease caspase-1. After being assembled, the NLRP3 inflammasome can trigger caspase-1 to induce gasdermin D (GSDMD)-dependent pyroptosis, promoting the maturation and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1 (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18). Recent studies have revealed that a variety of viruses activate or inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome via viral particles, proteins, and nucleic acids. In this review, we present a variety of regulatory mechanisms and functions of the NLRP3 inflammasome upon RNA viral infection and demonstrate multiple therapeutic strategies that target the NLRP3 inflammasome for anti-inflammatory effects in viral infection.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; RNA virus; inflammation; pyroptosis; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2024 Yue, Zhang, Gu, Liu, Lan, Liu, Li, Yang, Wan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sendai Virus V Protein Inhibits the Secretion of Interleukin-1β by Preventing NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e00842-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00842-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30021903 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA- and TRIM25-Binding Domains of Influenza Virus NS1 Protein Are Essential for Suppression of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Interleukin-1β Secretion.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):4105-4114. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00120-16. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26865721 Free PMC article.
-
The zebrafish NLRP3 inflammasome has functional roles in ASC-dependent interleukin-1β maturation and gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 24;295(4):1120-1141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011751. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31852739 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110542. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110542. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32738636 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein long-term effect on neuro-PASC.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Dec 18;18:1481963. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1481963. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39744674 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of NLRP3 Inflammasome on Osteoblasts and Osteogenic Differentiation: A Literature Review.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 29;17:2639-2653. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S457927. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38707958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Long COVID-Part 2: Understanding the Impact of Spike Protein and Cellular Receptor Interactions on the Pathophysiology of Long COVID Syndrome.Viruses. 2025 Apr 25;17(5):619. doi: 10.3390/v17050619. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and the NLRP3 Inflammasome: Focus on Female Fertility and Reproductive Health.Cells. 2025 Jan 2;14(1):36. doi: 10.3390/cells14010036. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39791737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome and single-cell profiling of the mechanism of diabetic kidney disease.World J Diabetes. 2025 Feb 15;16(2):101538. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i2.101538. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39959271 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

