An evolutionary game study on the collaborative governance of environmental pollution: from the perspective of regulatory capture
- PMID: 38249382
- PMCID: PMC10796718
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1320072
An evolutionary game study on the collaborative governance of environmental pollution: from the perspective of regulatory capture
Abstract
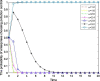
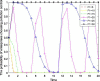
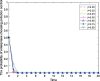
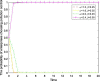
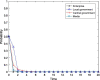
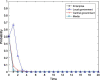
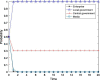
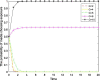
Local governments have been captured by enterprises and, thus, have relaxed environmental regulations. This phenomenon has occurred repeatedly and has resulted in serious environmental pollution, posing an enormous threat to public health. To solve this problem, this study introduces central environmental protection inspection and media supervision and considers the economic preferences and environmental preferences of local governments. A four-party evolutionary game model composed of enterprises, local governments, the central government and the media is constructed, and the equilibrium solution of four-party replicator dynamics equations is obtained. The influence of relevant parameters on the choice of strategies of the four main bodies is simulated by using MATLAB software to explore the paths and measures for overcoming regulatory capture and to further improve the modern environmental governance system. The results show the following: First, local governments are easily captured by large enterprises. Second, the central government can improve the environmental behavior of local governments by reducing their economic preferences and strengthening punishment. Third, compared to the penalties imposed by the central government, those imposed by local governments have a more significant impact on the environmental behaviors of enterprises. Fourth, compared to the use of an environmental protection tax policy or a tax relief policy alone, the combination of the two has a more significant impact on the environmental behaviors of enterprises. Fifth, central environmental protection inspection and media supervision can improve the environmental behaviors of both local governments and enterprises, and the effect of media supervision is better than that of central environmental protection inspection. This study recommends improving the performance evaluation system for local governments to coordinate economic development and environmental protection, ensuring that local governments assume the main responsibility, using a combination of incentive and constraint policies for enterprises, and increasing the environmental protection inspection and media supervision of local governments and enterprises to resolve the dilemma of regulatory capture in environmental pollution through the simultaneous enhancement of the environmental behavior of local governments and enterprises.
Keywords: collaborative governance; environment and public health; environmental pollution; four-party evolutionary game; regulatory capture.
Copyright © 2024 Hu, Wang, Zhang, Liao and Tao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
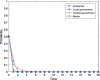
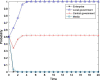
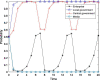
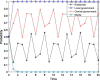
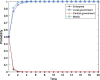
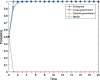
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary game analysis of factors influencing green innovation in Enterprises under environmental governance constraints.Environ Res. 2024 May 1;248:118095. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.118095. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38272295
-
Evolutionary game analysis on industrial pollution control of local government in China.J Environ Manage. 2021 Nov 15;298:113499. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113499. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Environ Manage. 2021. PMID: 34385115
-
Environmental Regulation, Greenwashing Behaviour, and Green Governance of High-Pollution Enterprises in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 1;19(19):12539. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912539. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231837 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship among Government, Enterprise, and Public in Environmental Governance from the Perspective of Multi-Player Evolutionary Game.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 11;16(18):3351. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183351. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31514308 Free PMC article.
-
Annex: Executive Summary and Health Deal.2016 Oct 23. In: Close JP, editor. AiREAS: Sustainocracy for a Healthy City: Phase 3: Civilian Participation – Including the Global Health Deal Proposition [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2016. Chapter 8. 2016 Oct 23. In: Close JP, editor. AiREAS: Sustainocracy for a Healthy City: Phase 3: Civilian Participation – Including the Global Health Deal Proposition [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2016. Chapter 8. PMID: 29787102 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Shi Y, Tang AD, Yao TS. A study on inter-provincial environmental pollution movement in China based on the input-output method. Energies. (2022) 15:6782. doi: 10.3390/en15186782 - DOI
-
- Li L, Song Y, Zhang ZQ. A tripartite game analysis of environmental pollution control based on complicated intergovernmental relations. Complexity. (2021) 2021:1–28. doi: 10.1155/2021/8148799 - DOI
-
- Gao FF, Xin BG. Effects of eco-environmental damage compensation system with multi-stakeholder engagements: a DSGE perspective from China. Environ Res Commun. (2022) 4:15001. doi: 10.1088/2515-7620/ac4877 - DOI
-
- Cheng ZC, Chen XY, Wen HW. How does environmental protection tax affect corporate environmental investment? Evidence from Chinese listed enterprises. Sustainability. (2022) 14:2932. doi: 10.3390/su14052932 - DOI
-
- Sun XK, Zhang CY. Environmental protection tax and total factor productivity-evidence from Chinese listed companies. Front Environ Sci. (2023) 10:1104439. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.1104439 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

