Role of probiotics in managing various human diseases, from oral pathology to cancer and gastrointestinal diseases
- PMID: 38249451
- PMCID: PMC10797027
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1296447
Role of probiotics in managing various human diseases, from oral pathology to cancer and gastrointestinal diseases
Abstract
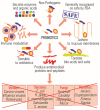
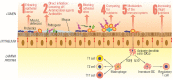
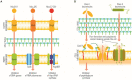
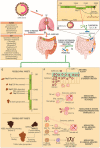
The imbalance of microbial composition and diversity in favor of pathogenic microorganisms combined with a loss of beneficial gut microbiota taxa results from factors such as age, diet, antimicrobial administration for different infections, other underlying medical conditions, etc. Probiotics are known for their capacity to improve health by stimulating the indigenous gut microbiota, enhancing host immunity resistance to infection, helping digestion, and carrying out various other functions. Concurrently, the metabolites produced by these microorganisms, termed postbiotics, which include compounds like bacteriocins, lactic acid, and hydrogen peroxide, contribute to inhibiting a wide range of pathogenic bacteria. This review presents an update on using probiotics in managing and treating various human diseases, including complications that may emerge during or after a COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: dysbiosis; gut microbiota; intestinal barrier; microbiome therapeutics; probiotics.
Copyright © 2024 Petrariu, Barbu, Niculescu, Constantin, Grigore, Cristian, Mihaescu and Vrancianu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adiki S. K., Perla C. K., Saha G., Katakam P., Theendra V. (2019). Enhancement in iron absorption on intake of chemometrically optimized ratio of probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum 299v with iron supplement pearl millet. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 190, 150–156. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1541-5, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agossa K., Dubar M., Lemaire G., Blaizot A., Catteau C., Bocquet E., et al. (2022). Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri on gingival inflammation and composition of the oral microbiota in patients undergoing treatment with fixed orthodontic appliances: study protocol of a randomized control trial. Pathogens 11:112. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020112, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

