The impact of mass vaccination policy and control measures on lumpy skin disease cases in Thailand: insights from a Bayesian structural time series analysis
- PMID: 38249552
- PMCID: PMC10797105
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1301546
The impact of mass vaccination policy and control measures on lumpy skin disease cases in Thailand: insights from a Bayesian structural time series analysis
Abstract
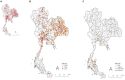
Introduction: In 2021, Thailand reported the highest incidence of lumpy skin disease (LSD) outbreaks in Asia. In response to the widespread outbreaks in cattle herds, the government's livestock authorities initiated comprehensive intervention measures, encompassing control strategies and a national vaccination program. Yet, the efficacy of these interventions remained unevaluated. This research sought to assess the nationwide intervention's impact on the incidence of new LSD cases through causal impact analysis.
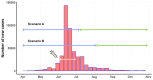
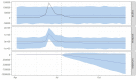
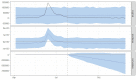
Methods: Data on weekly new LSD cases in Thailand from March to September 2021 was analyzed. The Bayesian structural time series (BSTS) analysis was employed to evaluate the causal relationship between new LSD cases in the pre-intervention phase (prior to the vaccination campaign) and the post-intervention phase (following the vaccination campaign). The assessment involved two distinct scenarios, each determined by the estimated effective intervention dates. In both scenarios, a consistent decline in new LSD cases was observed after the mass vaccination initiative, while other control measures such as the restriction of animal movement, insect control, and the enhancement of the active surveillance approach remained operational throughout the pre-intervention and the post-intervention phases.
Results and discussion: According to the relative effect results obtained from scenario A and B, it was observed that the incidence of LSD cases exhibited reductions of 119% (95% Credible interval [CrI]: -121%, -38%) and 78% (95% CrI: -126, -41%), respectively. The BSTS results underscored the significant influence of these interventions, with a Bayesian one-sided tail-area probability of p < 0.05. This model-based study provides insight into the application of BSTS in evaluating the impact of nationwide LSD vaccination based on the national-level data. The present study is groundbreaking in two respects: it is the first study to quantify the causal effects of a mass vaccination intervention on the LSD outbreak in Thailand, and it stands as the only endeavor of its kind in the Asian context. The insights collected from this study hold potential value for policymakers in Thailand and other countries at risk of LSD outbreaks.
Keywords: Bayesian structural time series; Thailand; causal impact; intervention; lumpy skin disease; mass vaccination.
Copyright © 2024 Punyapornwithaya, Arjkumpa, Buamithup, Jainonthee, Salvador and Jampachaisri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parvin R, Chowdhury EH, Islam MT, Begum JA, Nooruzzaman M, Globig A, et al. Clinical epidemiology, pathology, and molecular investigation of lumpy skin disease outbreaks in bangladesh during 2020–2021 indicate the re-emergence of an old African strain. Viruses. (2022) 14:2529. 10.3390/v14112529 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

