Defense against oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans by dark tea
- PMID: 38249557
- PMCID: PMC10796627
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1342747
Defense against oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans by dark tea
Abstract
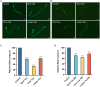
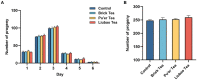
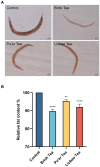
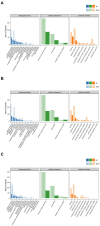
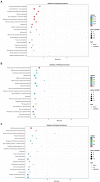
Dark tea, rich in nutricines including tea polyphenols and free amino acids, is a kind of post-fermented tea. The potential application of nutricines against oxidative damage and senescence, which drives animal health maintenance and disease prevention, has attracted considerable interest. In this study, the effect of dark tea and its effects on longevity and defense against oxidative stress was investigated in the Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) model. Under normal conditions, dark tea extended the lifespan without significant impairment of propagation. It also improved the motility, alleviated the fat accumulation and apoptosis. Additionally, orally administered dark tea could significantly decrease the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and resulted in a superior lifespan in H2O2-induced oxidative stressed C. elegans. In antioxidant assays in vitro, dark tea was found to be rich in strong hydroxyl, DPPH and ABTS+ free radical scavenging capacity. Interestingly, mRNA sequence analyses further revealed that dark tea may catalyze intracellular relevant oxidative substrates and synthesize antioxidants through synthetic and metabolic pathways. These results suggest that dark tea is worth further exploration as a potential dietary supplement for the maintenance of animal health and the prevention of related diseases.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; dark tea; longevity; mRNA sequencing analysis; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Ge and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


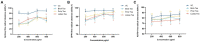



Similar articles
-
Two new catechins from Zijuan green tea enhance the fitness and lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via insulin-like signaling pathways.Food Funct. 2022 Sep 22;13(18):9299-9310. doi: 10.1039/d2fo01795d. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 35968754
-
Leaf extract of Caesalpinia mimosoides enhances oxidative stress resistance and prolongs lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jul 8;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2578-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31286949 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of aspalathin from rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) on acute oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans.Phytomedicine. 2013 Feb 15;20(3-4):380-6. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23218401
-
Oxidative stress-induced diseases and tea polyphenols.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 14;8(46):81649-81661. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20887. eCollection 2017 Oct 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29113421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Role of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Antiphotoaging, Stress Resistance, Neuroprotection, and Autophagy.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 23;11(2):474. doi: 10.3390/nu11020474. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30813433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Power of Fermented Tea to Improve Gut Microbiota and Combat Obesity Epidemic.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;13(10):779. doi: 10.3390/biology13100779. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Erdemli Z, Erdemli ME, Gul M, Altinoz E, Gul S, Kocaman G, et al. . Ameliorative effects of crocin on the inflammation and oxidative stress-induced kidney damages by experimental periodontitis in rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2021) 24:825–32. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2021.55875.12499, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

