Mucosal Immunity Related to CD8+ T Lymphocytes in Children with Helicobacter pylori Gastritis
- PMID: 38249639
- PMCID: PMC10796262
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2024.27.1.26
Mucosal Immunity Related to CD8+ T Lymphocytes in Children with Helicobacter pylori Gastritis
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the role of CD8+T cells as host immune factors in pediatric patients with Helicobacter pylori gastritis.
Methods: Gastric mucosal tissue and blood samples were collected from 39 children, including 11 children with H. pylori infection and 28 children as controls. Anti-CD8 and anti-T-bet antibodies were used for immunohistochemistry of the gastric mucosa. For the cell surface and intracellular staining, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with anti-IL7Rα, anti-CX3CR1, anti-CD8, anti-T-bet, and anti-IFN-γ antibodies. Cytokines of sera such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and CX3CL1 were analyzed using enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
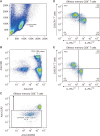
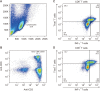
Results: In the immunohistochemistry of gastric mucosa, the frequency of CD8+ and T-bet+ T cells cells was higher in the H. pylori-positive group than in the control group (26.9± 7.8% vs. 16.9±3.3%, p<0.001; 5.0±2.5% vs. 2.2±0.7%, p=0.001). Between the control and H. pylori-positive groups, the frequency of IL-7RαlowCX3CR1+ CD8+ and T-bet+ INF-γ+ CD8+ T cells were not significantly different between surface and intracellular staining, respectively (40.4±24.0% vs. 38.2±17.8%, p=0.914; 40.4±24.0% vs. 38.2±17.8%, p=0.914). In the ELISA, no significant differences in TNF-α and CX3CL1 concentrations were observed between the control and H. pylori-positive groups (34.3±12.1 pg/mL vs. 47.0±22.6 pg/mL, p=0.114/0.5± 0.1 pg/mL vs. 0.5±0.1 pg/mL, p=0.188).
Conclusion: CD8+ T and Th1 cells, which secrete IFN-γ, might play important roles in the mucosal immunity of the stomach in children with H. pylori infection.
Keywords: Child; Gastritis; Helicobacter pylori; T-lymphocyte.
Copyright © 2024 by The Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concentrations of gastric mucosal cytokines in children with food allergy and Helicobacter pylori infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Nov 21;11(43):6751-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6751. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16425379 Free PMC article.
-
gammadelta T cells increase with gastric mucosal interleukin (IL)-7, IL-1beta, and Helicobacter pylori urease specific immunoglobulin levels via CCR2 upregulation in Helicobacter pylori gastritis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Jan;21(1 Pt 1):32-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04148.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16706809
-
[CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in gastric mucosa in children infected with Helicobacter pylori].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Jun;43(6):453-6. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16053734 Chinese.
-
[The regulatory function of tumor-infiltrating Th9 cells to anti-tumor activity of CD8(+) T cells in patients with gastric cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 23;44(11):1186-1193. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200530-00499. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36380667 Chinese.
-
Interplay between Helicobacter pylori and immune cells in immune pathogenesis of gastric inflammation and mucosal pathology.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 Jul;7(4):255-9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.2. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20190789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim BJ, Kim JG. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of Helicobacter pylori infections in Korea. Korean J Med. 2015;89:133–141.
-
- Maciorkowska E, Kasacka I, Kondej-Muszyńska K, Kaczmarski M, Kemona A. Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD8+) in the antrum mucosa in children with chronic Helicobacter pylori-related inflammation before and after bacteria eradication. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst. 2004;49(Suppl 1):216–218. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous