Evasion of host defense by Brucella
- PMID: 38250017
- PMCID: PMC10797155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100143
Evasion of host defense by Brucella
Abstract
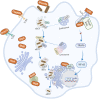
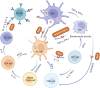
Brucella, an adept intracellular pathogen, causes brucellosis, a zoonotic disease leading to significant global impacts on animal welfare and the economy. Regrettably, there is currently no approved and effective vaccine for human use. The ability of Brucella to evade host defenses is essential for establishing chronic infection and ensuring stable intracellular growth. Brucella employs various mechanisms to evade and undermine the innate and adaptive immune responses of the host through modulating the activation of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), inflammatory responses, or the activation of immune cells like dendritic cells (DCs) to inhibit antigen presentation. Moreover, it regulates multiple cellular processes such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, and autophagy to establish persistent infection within host cells. This review summarizes the recently discovered mechanisms employed by Brucella to subvert host immune responses and research progress on vaccines, with the aim of advancing our understanding of brucellosis and facilitating the development of more effective vaccines and therapeutic approaches against Brucella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that the manuscript was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be considered as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Cited by
-
Role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in chronic brucellosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 30;14:1347883. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1347883. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38352057 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT2 inhibition enhances mitochondrial apoptosis in Brucella-infected bovine placental trophoblast cells.Vet Res. 2025 May 2;56(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01518-8. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40317067 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in brucellosis immune regulation inflammatory mechanisms and diagnostic advances.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Sep 1;30(1):830. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-03068-3. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40890848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of a multi-Epitope mRNA vaccine against Brucella type IV secretion system using reverse vaccinology and immunogenicity approaches.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 21;15(1):30698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09509-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40841725 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a 23S rRNA assay for Brucella and its application in evaluating bacterial growth status.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Feb 21;49(2):110. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10676-1. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 39982617
References
-
- Ali A., Waris A., Khan M.A., Asim M., Khan A.U., Khan S., et al. Recent advancement, immune responses, and mechanism of action of various vaccines against intracellular bacterial infections. Life Sciences. 2023;314 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

