Keratinocyte-to-macrophage communication exacerbate psoriasiform dermatitis via LRG1-enriched extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 38250043
- PMCID: PMC10797285
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.89180
Keratinocyte-to-macrophage communication exacerbate psoriasiform dermatitis via LRG1-enriched extracellular vesicles
Abstract
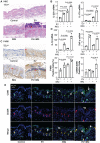
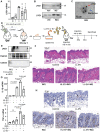
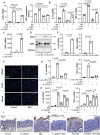
Rationale: Macrophage-associated inflammation and keratinocytes excessive proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion induced by stimulation play an important role in the progression of psoriasiform dermatitis. However, how these two types of cells communicate remains obscure. Methods: We induced a mouse model with experimental psoriasiform dermatitis by Imiquimod (IMQ). To investigate whether damaged keratinocytes promote macrophage polarization and accelerate skin lesions by releasing extracellular vesicle (EV), purified EV were isolated from the primary epidermis of 5-day IMQ-induced psoriasiform dermatitis model mice, and then fluorescence-labeled the EV with PKH67. The EV was injected into the skin of mice treated with IMQ or vehicle 2 days in situ. In addition, we established a co-culture system of the human monocytic cell line (THP-1) and HaCaT, and THP-1/HaCaT conditioned media culture model in vitro respectively. Subsequently, we evaluated the effect of Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1 (LRG1)-enriched EV on macrophage activation. Results: We demonstrated macrophages can significantly promote keratinocyte inflammation and macrophage polarization may be mediated by intercellular communication with keratinocytes. Interestingly, IMQ-induced 5-day, keratinocyte-derived EV recruited macrophage and enhanced the progression of skin lesions. Similar to results in vivo, EV released from M5-treated HaCaT significantly promotes Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) expression of THP-1 cells. Importantly, we found that LRG1-enriched EV regulates macrophages via TGF beta Receptor 1 (TGFβR1) dependent process. Conclusion: Our findings indicated a novel mechanism for promoting psoriasiform dermatitis, which could be a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicle; Keratinocyte.; Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1; Macrophage; Psoriasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, Barker J. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397:1301–15. - PubMed
-
- Boehncke WH, Schon MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983–94. - PubMed
-
- Ni X, Lai Y. Keratinocyte: A trigger or an executor of psoriasis? J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108:485–91. - PubMed
-
- Leite Dantas R, Masemann D, Schied T, Bergmeier V, Vogl T, Loser K. et al. Macrophage-mediated psoriasis can be suppressed by regulatory T lymphocytes. J Pathol. 2016;240:366–77. - PubMed
-
- Kuraitis D, Rosenthal N, Boh E, McBurney E. Macrophages in dermatology: pathogenic roles and targeted therapeutics. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;314:133–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

