Study of the utilization of main crop straw resources in Southern China and its potential as a replacement for chemical fertilizers
- PMID: 38250439
- PMCID: PMC10796737
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1172689
Study of the utilization of main crop straw resources in Southern China and its potential as a replacement for chemical fertilizers
Abstract
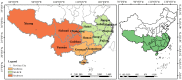
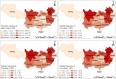
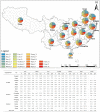
Although straw returning to the field (SRTTF) is conducive to promoting sustainable agricultural production and protecting the environment, straw resources are still wasted due to the lack of suitable straw-returning technology in southern China. Based on the statistical yearbook and a large number of studies, different methods were used to calculate the total straw resources and SRTTF potential, and differences in these methods were compared. The results indicate that the total amount of straw resources in southern China in 2021 was 3.35×108 t. The nutrient content of K2O in the straw accounted for the highest proportion of total nutrient resources (63.66%), followed by N (26.88%) and P2O5 (9.46%). In theory, total SRTTF could replace almost all K2O and part of N and P2O5, indicating that the nutrient substitution potential of SRTTF was high. It is suggested that the SRTTF method be adopted in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, which mainly uses direct returning (DR) supplemented by indirect returning (IDR). In southeast China, straw returning is carried out by the combination of IDR and IR. In southwest China, straw returning is mainly carried out by IR and supplemented by MDR. This study will provide theoretical support for the government to formulate straw-returning policy.
Keywords: quantity of straw; K2O; P2O5; chemical fertilizer; nitrogen; nutrient.
Copyright © 2024 Mu, Xu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Temporal and Spatial Distribution, Utilization Status, and Carbon Emission Reduction Potential of Straw Resources in China].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023 Feb 8;44(2):1149-1162. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201033. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 36775637 Chinese.
-
Potential of crop straw incorporation for replacing chemical fertilizer and reducing nutrient loss in Sichuan Province, China.Environ Pollut. 2023 Mar 1;320:121034. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121034. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 36623790
-
Impacts of Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Organic Carbon Composition, Enzyme Activity, and Grain Yield in Wheat-Maize Rotation.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 18;13(9):1929. doi: 10.3390/life13091929. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763332 Free PMC article.
-
Does straw returning affect the root rot disease of crops in soil? A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Environ Manage. 2023 Jun 15;336:117673. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117673. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Environ Manage. 2023. PMID: 36933512
-
[Effects of organic manure on soil nutrient content: A review].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2020 Apr;31(4):1403-1416. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202004.025. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32530216 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Estimating thresholds of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer rates for rice cropping systems in China.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Sep 12;15:1470774. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1470774. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39328794 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid production from corn straw by cellobiohydrolase and delta-6 desaturase engineered Mucor circinelloides strains under solid state fermentation.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 13;14(1):18784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68499-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39138250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi Y. Y., Gao C. Y., Wang H. Y., Wang Y. J. (2019). A summarization of the national regulation on crop straw utilization and burning prohibition and the corresponding legislative proposal. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Regional. Planning. 40 (08), 1–10.
-
- Cheng Z. Y., Jia Y. K., Bai Y. Y., Zhang T. Z., Ren K., Zhou X. Y., et al. (2023). Intensifying the environmental performance of chicken meat production in China: From perspective of life cycle assessment. J. Cleaner. Production. 384, 135603. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135603 - DOI
-
- Cui S., Song Z. H., Zhang L. M., Shen Z. X., Hough R., Zhang Z. L., et al. (2021). Spatial and temporal variations of open straw burning based on fire spots in northeast China from 2013 to 2017. Atmospheric. Environ. 244, 117962. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117962 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

