Deep learning for medicinal plant species classification and recognition: a systematic review
- PMID: 38250440
- PMCID: PMC10796487
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1286088
Deep learning for medicinal plant species classification and recognition: a systematic review
Abstract
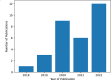
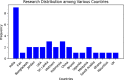
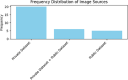
Knowledge of medicinal plant species is necessary to preserve medicinal plants and safeguard biodiversity. The classification and identification of these plants by botanist experts are complex and time-consuming activities. This systematic review's main objective is to systematically assess the prior research efforts on the applications and usage of deep learning approaches in classifying and recognizing medicinal plant species. Our objective was to pinpoint systematic reviews following the PRISMA guidelines related to the classification and recognition of medicinal plant species through the utilization of deep learning techniques. This review encompassed studies published between January 2018 and December 2022. Initially, we identified 1644 studies through title, keyword, and abstract screening. After applying our eligibility criteria, we selected 31 studies for a thorough and critical review. The main findings of this reviews are (1) the selected studies were carried out in 16 different countries, and India leads in paper contributions with 29%, followed by Indonesia and Sri Lanka. (2) A private dataset has been used in 67.7% of the studies subjected to image augmentation and preprocessing techniques. (3) In 96.7% of the studies, researchers have employed plant leaf organs, with 74% of them utilizing leaf shapes for the classification and recognition of medicinal plant species. (4) Transfer learning with the pre-trained model was used in 83.8% of the studies as a future extraction technique. (5) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is used by 64.5% of the paper as a deep learning classifier. (6) The lack of a globally available and public dataset need for medicinal plants indigenous to a specific country and the trustworthiness of the deep learning approach for the classification and recognition of medicinal plants is an observable research gap in this literature review. Therefore, further investigations and collaboration between different stakeholders are required to fulfilling the aforementioned research gaps.
Keywords: classification; deep learning; medicinal plant dataset; medicinal plant species; recognition.
Copyright © 2024 Mulugeta, Sharma and Mesfin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced classification of medicinal plants using deep learning and optimized CNN architectures.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 30;11(3):e42385. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42385. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39991214 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for Ethiopian indigenous medicinal plant species identification and classification.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024 Nov-Dec;15(6):100987. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2024.100987. Epub 2024 Nov 14. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39546923 Free PMC article.
-
HybNet: A hybrid deep models for medicinal plant species identification.MethodsX. 2024 Dec 21;14:103126. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.103126. eCollection 2025 Jun. MethodsX. 2024. PMID: 39830878 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Applied for Prediction of Plant Leaf Diseases.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 12;21(14):4749. doi: 10.3390/s21144749. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plants used to treat diabetes in Sri Lankan Siddha Medicine - An ethnopharmacological review of historical and modern sources.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:531-599. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.053. Epub 2016 Jul 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27448453 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced classification of medicinal plants using deep learning and optimized CNN architectures.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 30;11(3):e42385. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42385. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39991214 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the climate change impact on Epimedium brevicornu in China with the MaxEnt model.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 16;16:1534608. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1534608. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40589949 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based classification of traditional Chinese medicine: a novel approach.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Aug 1;15(8):7483-7496. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1354. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40785942 Free PMC article.
-
The Millennia-Long Development of Drugs Associated with the 80-Year-Old Artificial Intelligence Story: The Therapeutic Big Bang?Molecules. 2024 Jun 7;29(12):2716. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122716. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdollahi J. (Ed.) (2022). “Identification of Medicinal Plants in Ardabil Using Deep learning: Identification of Medicinal Plants using Deep learning,” in 2022 27th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC), 2022 23-24 Feb, Tehran, Iran. (IEEE; ). doi: 10.1109/CSICC55295.2022.9780493 - DOI
-
- Akter R., Hosen M. I. (Eds.) (2020). “CNN-based leaf image classification for Bangladeshi medicinal plant recognition,” in 2020 Emerging Technology in Computing, Communication and Electronics (ETCCE), 2020 21-22 Dec, Bangladesh. (IEEE; ). doi: 10.1109/ETCCE51779.2020.9350900 - DOI
-
- Almazaydeh L., Alsalameen R., Elleithy K. (2022). Herbal leaf recognition using mask-region convolutional neural network (MASK R-CNN). J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 100 (11), 3664–3671.
-
- Al-Qurran R., Al-Ayyoub M., Shatnawi A. (2022). Plant classification in the wild: Energy evaluation for deep learning models. Multimedia Tools Applications 81 (21), 30143–30167. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12695-5 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

