The Ability of Antibody against Truncated Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Peptide to Evaluate the Native Protein on Tear Drops of Dry Eye Disease Patients by a Point-of-Care Diagnostic System
- PMID: 38250498
- PMCID: PMC10795817
- DOI: 10.4103/joco.joco_320_22
The Ability of Antibody against Truncated Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Peptide to Evaluate the Native Protein on Tear Drops of Dry Eye Disease Patients by a Point-of-Care Diagnostic System
Abstract
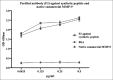
Purpose: To obtain a reactive and specific antibody against truncated matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), that has reactivity toward the native protein. Precision, accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity were evaluated using a point-of-care test.
Methods: An in silico study was used to confirm the anti peptide truncated MMP-9 is against native MMP-9. After an antibody titer assessment, purification, and characterization, the anti MMP-9 was assessed. The cut-off value was determined using the purified gelatinases of the supernatant HCT 116 cell line. The supernatant was purified by preparative native-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis based on charge and size of the proteins. Furthermore, quality control (QC) of the results were performed following standard densitometry methods.
Results: A truncated MMP-9 is the major epitope peptide that can trigger the immune system to scavenge for a specific and reactive antibody against the native MMP-9. The MMP-9 native protein is purified from the supernatant of the HCT 116 cell line and the commercially available, full-length MMP-9. The cut-off value was estimated at 30 μg/mL. QC results indicated that the specificity was 80%, sensitivity was 96.7%, accuracy was 91%, and precision was 91.66%. The area under curve was 0.827 (P < 0.001). The positive predictive value was 83%, and the negative predictive value was 96%.
Conclusions: The antibody against the synthetic epitope peptide can detect the native MMP-9. Native MMP-9 is considered the main biomarker in an immunoassay POCT and is used to diagnose dry eye disease (DED). In accordance with QC results, MMP-9 point of care test can be utilized for screening patients suffering from DED.
Keywords: Dry eye disease; Epitope peptide; In silico analysis; Matrix metalloproteinase 9 point-of-care test; Polyclonal antibody.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Current Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Testing in Dry Eye Disease Using a Commercially Available Point-of-Care Immunoassay.Ophthalmology. 2016 Nov;123(11):2300-2308. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.07.028. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Ophthalmology. 2016. PMID: 27665213
-
Comparative Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Immunoassay and Tear Osmolarity Measurement for Diagnosing Severity of Dry Eye Disease.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2023 Oct;37(5):409-416. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2023.0062. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37621090 Free PMC article.
-
Dichotomous versus 5-scale grading system for the interpretation of the point-of-care immunoassay for tear matrix metalloproteinase-9 in dry eye.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 13;13(1):6085. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32928-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37055446 Free PMC article.
-
The Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Point-of-Care Test in Dry Eye.Ocul Surf. 2016 Apr;14(2):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2015.10.004. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Ocul Surf. 2016. PMID: 26850527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) for the management of hematological malignancies.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Nov 5;223:113623. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113623. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34157437 Review.
References
-
- Tsubota K. Short tear film breakup time-type dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59:S64–70. - PubMed
-
- Cauwe B, Opdenakker G. Intracellular substrate cleavage: A novel dimension in the biochemistry, biology and pathology of matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;45:351–423. - PubMed
-
- Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Opdenakker G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;37:375–536. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
