Phylogenetic conservation of Trop-2 across species-rodent and primate genomics model anti-Trop-2 therapy for pre-clinical benchmarks
- PMID: 38250577
- PMCID: PMC10797630
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1297367
Phylogenetic conservation of Trop-2 across species-rodent and primate genomics model anti-Trop-2 therapy for pre-clinical benchmarks
Abstract
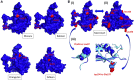
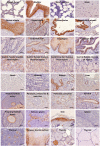
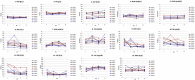
A phylogenetic conservation analysis of Trop-2 across vertebrate species showed a high degree of sequence conservation, permitting to explore multiple models as pre-clinical benchmarks. Sequence divergence and incomplete conservation of expression patterns were observed in mouse and rat. Primate Trop-2 sequences were found to be 95%-100% identical to the human sequence. Comparative three-dimension primate Trop-2 structures were obtained with AlphaFold and homology modeling. This revealed high structure conservation of Trop-2 (0.66 ProMod3 GMQE, 0.80-0.86 ± 0.05 QMEANDisCo scores), with conservative amino acid changes at variant sites. Primate TACSTD2/TROP2 cDNAs were cloned and transfectants for individual ORF were shown to be efficiently recognized by humanized anti-Trop-2 monoclonal antibodies (Hu2G10, Hu2EF). Immunohistochemistry analysis of Macaca mulatta (rhesus monkey) tissues showed Trop-2 expression patterns that closely followed those in human tissues. This led us to test Trop-2 targeting in vivo in Macaca fascicularis (cynomolgus monkey). Intravenously injected Hu2G10 and Hu2EF were well tolerated from 5 to 10 mg/kg. Neither neurological, respiratory, digestive, urinary symptoms, nor biochemical or hematological toxicities were detected during 28-day observation. Blood serum pharmacokinetic (PK) studies were conducted utilizing anti-idiotypic antibodies in capture-ELISA assays. Hu2G10 (t1/2 = 6.5 days) and Hu2EF (t1/2 = 5.5 days) were stable in plasma, and were detectable in the circulation up to 3 weeks after the infusion. These findings validate primates as reliable models for Hu2G10 and Hu2EF toxicity and PK, and support the use of these antibodies as next-generation anti-Trop-2 immunotherapy tools.
Keywords: Trop-2; pharmacokinetics; phylogenetic conservation; primate genomics; toxicity.
Copyright © 2024 Guerra, Trerotola, Relli, Lattanzio, Boujnah, Travali, Moschella, Todaro, Pierdomenico, Di Pietro, Tinari and Alberti.
Conflict of interest statement
EG is an inventor in patents WO201687651 and WO201784763, and a partner in Mediterranea Theranostic Srl. MT is an inventor in patent WO201784763. SA is an inventor in patents WO201089782, WO201687651 and WO201784763, and is founder and CEO of Oncoxx Biotech Srl and Mediterranea Theranostic Srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

