Stable fixed points of combinatorial threshold-linear networks
- PMID: 38250671
- PMCID: PMC10795766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aam.2023.102652
Stable fixed points of combinatorial threshold-linear networks
Abstract
Combinatorial threshold-linear networks (CTLNs) are a special class of recurrent neural networks whose dynamics are tightly controlled by an underlying directed graph. Recurrent networks have long been used as models for associative memory and pattern completion, with stable fixed points playing the role of stored memory patterns in the network. In prior work, we showed that target-free cliques of the graph correspond to stable fixed points of the dynamics, and we conjectured that these are the only stable fixed points possible [1, 2]. In this paper, we prove that the conjecture holds in a variety of special cases, including for networks with very strong inhibition and graphs of size . We also provide further evi-dence for the conjecture by showing that sparse graphs and graphs that are nearly cliques can never support stable fixed points. Finally, we translate some results from extremal com-binatorics to obtain an upper bound on the number of stable fixed points of CTLNs in cases where the conjecture holds.
Keywords: 15; 34; 92; Collatz-Wielandt formula; attractor neural networks; cliques; stable fixed points; threshold-linear networks.
Figures
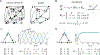
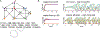
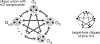

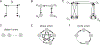
References
-
- Morrison K, Degeratu A, Itskov V, and Curto C. Diversity of emergent dynamics in competitive threshold-linear networks: a preliminary report. Available at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.04463
-
- Curto C, Geneson J, and Morrison K. Fixed points of competitive threshold-linear networks. Neural Comput, 31(1):94–155, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Amit Daniel J.. Modeling brain function: The world of attractor neural networks. Cambridge: University Press, 1989.
-
- Xie X, Hahnloser RH, and Seung HS. Selectively grouping neurons in recurrent networks of lateral inhibition. Neural Comput, 14:2627–2646, 2002. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
