Effects of Cu (II) on the Growth of Chlorella vulgaris and Its Removal Efficiency of Pollutants in Synthetic Piggery Digestate
- PMID: 38251012
- PMCID: PMC10819573
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12010056
Effects of Cu (II) on the Growth of Chlorella vulgaris and Its Removal Efficiency of Pollutants in Synthetic Piggery Digestate
Abstract
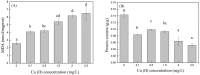
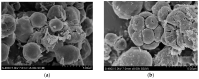
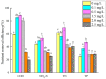
C. vulgaris has a positive effect on the removal of nutrients from pig farm biogas slurry. However, swine wastewater often contains heavy metal ions, such as Cu (II), which may have impacts on the nutrient removal performance of C. vulgaris. Additionally, the heavy metal ions in wastewater can be adsorbed by microalgae. In this study, the stress effect of Cu (II) on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris, the Cu (II) removal by microalgae, and the effect of different concentrations of Cu (II) on the nutrient removal efficiency of C. vulgaris in biogas slurries were explored. The results showed that the microalgae biomass of microalgae on the sixth day of the experiment was the highest in the treatment with a Cu (II) concentration of 0.5 mg/L, which was 30.1% higher than that of the 2.5 mg/L group. C. vulgaris had higher removal efficiencies of Cu (II) at a Cu (II) concentration of 0.1~1.5 mg/L. The-OH, C=O, -COOH, and C-O groups on the surface of the algal cells play a significant role in the removal of Cu (II). The removal rates of COD, NH3-N, TN, and TP by C. vulgaris at a Cu (II) concentration of 0.5 mg/L were the highest, which were 89.0%, 53.7%, 69.6%, and 47.3%, respectively.
Keywords: Chlorella vulgaris; Cu (II); piggery digestate; removal efficiency of pollutant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nutrient and heavy metal removal from piggery wastewater and CH4 enrichment in biogas based on microalgae cultivation technology under different initial inoculum concentration.Water Environ Res. 2020 Jun;92(6):922-933. doi: 10.1002/wer.1287. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Water Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 31837273
-
The effects of influent chemical oxygen demand and strigolactone analog concentration on integral biogas upgrading and pollutants removal from piggery wastewater by different microalgae-based technologies.Bioresour Technol. 2023 Feb;370:128483. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128483. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Bioresour Technol. 2023. PMID: 36513303
-
Induction of vitamin B12 to purify biogas slurry and upgrade biogas using co-culture of microalgae and fungi.Water Environ Res. 2021 Aug;93(8):1254-1262. doi: 10.1002/wer.1504. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Water Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 33372311
-
Effect of GR24 concentrations on tetracycline and nutrient removal from biogas slurry by different microalgae-based technologies.Bioresour Technol. 2023 Feb;369:128400. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128400. Epub 2022 Nov 26. Bioresour Technol. 2023. PMID: 36442601
-
Cultivation of two Chlorella species in Open sewage contaminated channel wastewater for biomass and biochemical profiles: Comparative lab-scale approach.J Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 20;344:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Nov 25. J Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34838946 Review.
References
-
- Wang M. The Effect and Mechanism of Bioaugmentation with Microalgal Bacterial Consortia on the Treatment of Piggery Digestate. Zhejiang University; Hangzhou, China: 2021.
-
- Wang Y.Z., Cheng P.F., Liu D.F., Liu T.Z. Purification Effect of Piggery Wastewater with Chlorella pyrenoidosa by Immobilized Biofilm-Attached Culture. Environ. Sci. 2017;38:3354–3361. - PubMed
-
- Pan Y.C., Sun C., Liu Y., Tang X.M., Ren Y.M. Carrying capacity of livestock and poultry breeding based on feces disposal volume of land. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015;31:232–239.
-
- Zhu L.D. Microalgal culture strategies for biofuel production: A review. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining. 2015;9:801–814. doi: 10.1002/bbb.1576. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

