Resonance Effects in Variable Practice for Handball, Basketball, and Volleyball Skills: A Study on Contextual Interference and Differential Learning
- PMID: 38251279
- PMCID: PMC10821429
- DOI: 10.3390/sports12010005
Resonance Effects in Variable Practice for Handball, Basketball, and Volleyball Skills: A Study on Contextual Interference and Differential Learning
Abstract
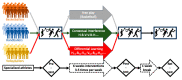
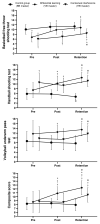
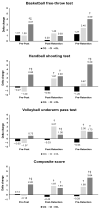
Effective sports training should be attuned to the athlete's specific conditionings and characteristics. In motor learning research, two often neglected factors that influence this resonance are the learner's athletic background and the structural diversity of exercises (e.g., relative similarity). In the setting of real-word training with higher external validity, this study examines the effects of three learning approaches (i.e., contextual interference (CI), differential learning (DL), and free-play control condition (CO)) on the parallel learning of handball (HB), volleyball (VB), and basketball (BB) skills, considering participants' prior sport backgrounds. Forty-five males (15 HB, 15 VB, and 15 BB players) with a mean age of 22 ± 1.4 years and at least 6 years of experience in the mastered discipline voluntarily participated in this study. A pre-post-retention test design including a 6-week-intervention program was employed. During the intervention period, participants engaged in three training sessions a week, with each one lasting approximately 80 min. Each of the three test sessions involved the execution of ten attempts of BB free-throw shooting, HB three-step goal throwing, and VB underarm passing following a blocked order. In terms of short-term (pre-post) gain, only the DL group significantly improved their performance in both non-mastered disciplines (p = 0.03, ES = 1.58 for the BB free-throw and p = 0.05, ES = 0.9 for the HB shooting tests), with a trend (ES = 0.53) towards an improvement in the performance of the mastered VB underarm-pass skill. In terms of relatively permanent gains, the CI group significantly improved their performances from pre- to retention test only in the non-mastered BB free-throw skill (p = 0.018, ES = 1.17). In contrast, the DL group significantly improved their performance at retention compared to the pre-test in both non-mastered BB (p = 0.004, ES = 1.65) and HB (p = 0.003, ES = 2.15) skills, with a trend (ES = 0.4) towards improvement in the mastered VB test. In both the short-term and relatively long-term, higher composite score gains were observed in DL compared to CI (p = 0.006, ES = 1.11 and 0.049, ES = 1.01) and CO (p = 0.001, ES = 1.73 and <0.0001, ES = 2.67). In conclusion, the present findings provide additional support for the potential advantages of the DL model over those of CI. These findings can serve as the basis for tailored training and intervention strategies and provide a new perspective for addressing various issues related to individual and situational learning.
Keywords: adaptive stochastic resonance; basketball free-throw; contextual interference; differential learning; free-play; handball shooting; movement topology; skill similarity; volleyball underarm pass.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Learning Multiple Movements in Parallel-Accurately and in Random Order, or Each with Added Noise?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 2;19(17):10960. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710960. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36078674 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Peripheral Vision on Manual Reaction Time Using Fitlight Technology for Handball, Basketball and Volleyball Players.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;10(6):697. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060697. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370628 Free PMC article.
-
Plyometric Training Improves Sprinting, Jumping and Throwing Capacities of High Level Female Volleyball Players Better Than Skill-Based Conditioning.J Sports Sci Med. 2017 Dec 1;16(4):527-535. eCollection 2017 Dec. J Sports Sci Med. 2017. PMID: 29238253 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of plyometric training on technical skill performance among athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 17;18(7):e0288340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288340. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37459333 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling individuality in the early phase of motor learning: a machine learning approach for analysing weightlifting technique in novices.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 30;12:1426058. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1426058. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39139294 Free PMC article.
-
Acute effects of motor learning models on technical efficiency in strength-coordination exercises: a comparative analysis of Olympic snatch biomechanics in beginners.Biol Sport. 2025 Jan;42(1):151-161. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2025.141662. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Biol Sport. 2025. PMID: 39758181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corrêa U.C., Benda R.N., de Oliveira D.L., Ugrinowitsch H., Freudenheim A.M., Tani G. Different Faces of Variability in the Adaptive Process of Motor Skill Learning. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2015;19:465–487. - PubMed
-
- Van Rossum J.H. Schmidt’s schema theory: The empirical base of the variability of practice hypothesis: A critical analysis. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1990;9:387–435. doi: 10.1016/0167-9457(90)90010-B. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

