Metastable States in the Hinge-Bending Landscape of an Enzyme in an Atomistic Cytoplasm Simulation
- PMID: 38252018
- PMCID: PMC11180962
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c03134
Metastable States in the Hinge-Bending Landscape of an Enzyme in an Atomistic Cytoplasm Simulation
Abstract
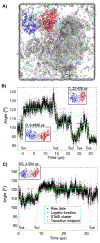
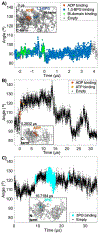
Many enzymes undergo major conformational changes to function in cells, particularly when they bind to more than one substrate. We quantify the large-amplitude hinge-bending landscape of human phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) in a human cytoplasm. Approximately 70 μs of all-atom simulations, upon coarse graining, reveal three metastable states of PGK with different hinge angle distributions and additional substates. The "open" state was more populated than the "semi-open" or "closed" states. In addition to free energies and barriers within the landscape, we characterized the average transition state passage time of ≈0.3 μs and reversible substrate and product binding. Human PGK in a dilute solution simulation shows a transition directly from the open to closed states, in agreement with previous SAXS experiments, suggesting that the cell-like model environment promotes stability of the human PGK semi-open state. Yeast PGK also sampled three metastable states within the cytoplasm model, with the closed state favored in our simulation.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar S; Ma B; Tsai C-J; Wolfson H; Nussinov R Folding Funnels and Conformational Transitions via Hinge-Bending Motions. Cell Biochem. Biophys 1999, 31, 141–164. - PubMed
-
- Biehl R; Richter D Slow Internal Protein Dynamics in Solution. J. Phys. Condens. Matter Inst. Phys. J 2014, 26, 503103. - PubMed
-
- McCammon JA; Gelin BR; Karplus M; Wolynes PG The Hinge-Bending Mode in Lysozyme. Nature 1976, 262, 325–326. - PubMed
-
- Haran G; Mazal H How Fast Are the Motions of Tertiary-Structure Elements in Proteins? J. Chem. Phys 2020, 153, 130902. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

