Global landscape of COVID-19 research: a visualization analysis of randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 38252392
- PMCID: PMC10803477
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-023-01254-3
Global landscape of COVID-19 research: a visualization analysis of randomized clinical trials
Abstract
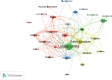
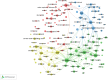
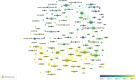
The emergence of COVID-19 in 2019 has resulted in a significant global health crisis. Consequently, extensive research was published to understand and mitigate the disease. In particular, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been considered the benchmark for assessing the efficacy and safety of interventions. Hence, the present study strives to present a comprehensive overview of the global research landscape pertaining to RCTs and COVID-19. A bibliometric analysis was performed using the Scopus database. The search parameters included articles published from 2020 to 2022 using keywords specifically related to COVID-19 and RCTs. The data were analyzed using various bibliometric indicators. The volume of publications, contributions of countries and institutions, funding agencies, active journals, citation analysis, co-occurrence analysis, and future research direction analysis were specifically analyzed. A total of 223,480 research articles concerning COVID-19 were published, with 3,727 of them related to RCTs and COVID-19. The ten most productive countries collectively produced 75.8% of the documents, with the United States leading the way by contributing 31.77%, followed by the UK with 14.03% (n = 523), China with 12.96% (n = 483) and Canada with 7.16% (n = 267). Trials (n = 173, 4.64%), BMJ Open (n = 81, 2.17%), PLOS One (n = 73, 1.96%) and JAMA Network Open (n = 53, 1.42%) were the most active journals in publishing articles related to COVID-19 RCTs. The co-occurrence analysis identified four clusters of research areas: the safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines, mental health strategies to cope with the impact of the pandemic, the use of monoclonal antibodies to treat patients with COVID-19, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses of COVID-19 research. This paper offers a detailed examination of the global research environment pertaining to RCTs and their use in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The comprehensive body of research findings was found to have been generated by the collaborative efforts of multiple countries, institutions, and funding organizations. The predominant research areas encompassed COVID-19 vaccines, strategies for mental health, monoclonal antibodies, and systematic reviews. This information has the potential to aid researchers, policymakers, and funders in discerning areas of weakness and establishing areas of priority.
Keywords: Bibliometric; COVID-19; Randomized controlled trials; Scopus; VOSviewer; Visualization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visualizing the landscape of urolithiasis research from 1979-2023: a global bibliometric analysis of randomized clinical trials.Urolithiasis. 2024 Oct 29;52(1):153. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01649-1. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 39470824
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Mapping trends and hotspots of research on COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of global research.J Infect Public Health. 2025 Jan;18(1):102597. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102597. Epub 2024 Nov 22. J Infect Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39603060
-
Research landscape on COVID-19 and liver dysfunction: A bibliometric analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 21;29(27):4356-4367. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i27.4356. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37545639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric study of the top 100 most-cited randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews and meta-analyses published in endodontic journals.Int Endod J. 2019 Sep;52(9):1297-1316. doi: 10.1111/iej.13131. Epub 2019 May 13. Int Endod J. 2019. PMID: 31009099 Review.
Cited by
-
Analyzing global research trends and focal points in the utilization of laser techniques for the treatment of urolithiasis from 1978 to 2022: visualization and bibliometric analysis.Urolithiasis. 2024 Apr 17;52(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01568-1. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 38630266 Review.
-
Establishing clinical research networks for future infectious disease outbreak responses in Southeast Asia: Report of a workshop on challenges and opportunities.IJID Reg. 2024 Nov 19;14:100494. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.100494. eCollection 2025 Mar. IJID Reg. 2024. PMID: 39737414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard, https://covid19.who.int/ (2023, accessed May 3 2023).
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Guidance on Conduct of Clinical Trials of Medical Products During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency, https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents... (2021, accessed April 30 2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

