NfL reliability across laboratories, stage-dependent diagnostic performance and matrix comparability in genetic FTD: a large GENFI study
- PMID: 38253362
- PMCID: PMC11347244
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2023-332464
NfL reliability across laboratories, stage-dependent diagnostic performance and matrix comparability in genetic FTD: a large GENFI study
Abstract
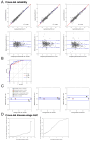
Background: Blood neurofilament light chain (NfL) is increasingly considered as a key trial biomarker in genetic frontotemporal dementia (gFTD). We aimed to facilitate the use of NfL in gFTD multicentre trials by testing its (1) reliability across labs; (2) reliability to stratify gFTD disease stages; (3) comparability between blood matrices and (4) stability across recruiting sites.
Methods: Comparative analysis of blood NfL levels in a large gFTD cohort (GENFI) for (1)-(4), with n=344 samples (n=148 presymptomatic, n=11 converter, n=46 symptomatic subjects, with mutations in C9orf72, GRN or MAPT; and n=139 within-family controls), each measured in three different international labs by Simoa HD-1 analyzer.
Results: NfL revealed an excellent consistency (intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) 0.964) and high reliability across the three labs (maximal bias (pg/mL) in Bland-Altman analysis: 1.12±1.20). High concordance of NfL across laboratories was moreover reflected by high areas under the curve for discriminating conversion stage against the (non-converting) presymptomatic stage across all three labs. Serum and plasma NfL were largely comparable (ICC 0.967). The robustness of NfL across 13 recruiting sites was demonstrated by a linear mixed effect model.
Conclusions: Our results underline the suitability of blood NfL in gFTD multicentre trials, including cross-lab reliable stratification of the highly trial-relevant conversion stage, matrix comparability and cross-site robustness.
Keywords: COGNITION; FRONTOTEMPORAL DEMENTIA; NEUROPSYCHIATRY.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). JK received speaker fees, research support, travel support, and/or served on advisory boards by Swiss MS Society, Swiss National Research Foundation (320030_189140/1), University of Basel, Progressive MS Alliance, Alnylam, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Immunic, Merck, Neurogenesis, Novartis, Octave Bioscience, Quanterix, Roche, Sanofi, Stata DX. MS has received consultancy honoraria from Ionis, UCB, Prevail, Orphazyme, Servier, Reata, GenOrph, AviadoBio, Biohaven, Zevra,and Lilly, all unrelated to the present manuscript. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
