The interaction between ageing and Alzheimer's disease: insights from the hallmarks of ageing
- PMID: 38254235
- PMCID: PMC10804662
- DOI: 10.1186/s40035-024-00397-x
The interaction between ageing and Alzheimer's disease: insights from the hallmarks of ageing
Abstract
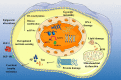
Ageing is a crucial risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and is characterised by systemic changes in both intracellular and extracellular microenvironments that affect the entire body instead of a single organ. Understanding the specific mechanisms underlying the role of ageing in disease development can facilitate the treatment of ageing-related diseases, such as AD. Signs of brain ageing have been observed in both AD patients and animal models. Alleviating the pathological changes caused by brain ageing can dramatically ameliorate the amyloid beta- and tau-induced neuropathological and memory impairments, indicating that ageing plays a crucial role in the pathophysiological process of AD. In this review, we summarize the impact of several age-related factors on AD and propose that preventing pathological changes caused by brain ageing is a promising strategy for improving cognitive health.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Anti-ageing therapy; Brain ageing; Cell senescence; Chronic inflammation; Hallmarks of ageing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Goikolea J, Gerenu G, Daniilidou M, Mangialasche F, Mecocci P, Ngandu T, et al. Serum Thioredoxin-80 is associated with age, ApoE4, and neuropathological biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: a potential early sign of AD. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022;14(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-00979-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 81873169/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82104967/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.2022RC1220/The Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- No. 2020JJ4803/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022JJ40728/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

