Development and Validation of an Auricular Acupuncture Protocol for the Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting in Cancer Patients
- PMID: 38255105
- PMCID: PMC10815809
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12020218
Development and Validation of an Auricular Acupuncture Protocol for the Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting in Cancer Patients
Abstract
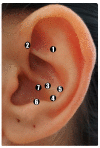
Auricular acupuncture (AA) has been used to manage chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). However, the application of the technique varies widely among the clinical trials that test its effectiveness. The aim of the present study was to develop and clinically validate an AA protocol for the management of CINV in cancer patients. This study was carried out in two stages: (1) development of the AA protocol for the management of CINV and (2) clinical validation of the protocol. The content validity of the protocol was determined by a panel of specialists, with an agreement rate ranging from 85.7% to 100%. In the clinical validation, when administered to cancer patients, the protocol developed has been shown to reduce the incidence, frequency, severity, and length of nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, as well as the severity of nausea and anticipatory nausea following chemotherapy. This protocol needs to be tested in future studies, including a pilot study with a sham group and a randomized clinical trial, in order to further evaluate its feasibility, acceptability, safety, and clinical usefulness for the management of CINV.
Keywords: auricular acupuncture; content validity; development and evaluation; nausea; oncology; palliative care; vomiting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Patel P., Robinson P.D., Wahib N., Cheung P., Wong T., Cabral S., Parker A., Cohen M., Devine K., Gibson P., et al. Interventions for the prevention of acute phase chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in adult and pediatric patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer. 2022;30:8855–8869. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07287-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

