Hyperglycaemia and Its Prognostic Value in Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to the Hospital in Lithuania
- PMID: 38255162
- PMCID: PMC10813648
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12010055
Hyperglycaemia and Its Prognostic Value in Patients with COVID-19 Admitted to the Hospital in Lithuania
Abstract
Background and objectives: Increased blood glucose levels atadmission are frequently observed in COVID-19 patients, even in those without pre-existing diabetes. Hyperglycaemia is associated with an increased incidence of severe COVID-19 infection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between hyperglycaemia at admission with the need for invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) and in-hospital mortality in patients without diabetes who were hospitalized for COVID-19 infection.
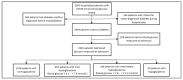
Materials and methods: This retrospective observational study was conducted at Vilnius University Hospital Santaros Clinics, Lithuania with adult patients who tested positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 and were hospitalized between March 2020 and May 2021. Depersonalized data were retrieved from electronic medical records. Based on blood glucose levels on the day of admission, patients without diabetes were divided into 4 groups: patients with hypoglycaemia (blood glucose below 4.0 mmol/L), patients with normoglycaemia (blood glucose between ≥4.0 mmol/L and <6.1 mmol/L), patients with mild hyperglycaemia (blood glucose between ≥6.1 mmol/L and <7.8 mmol/L), and patients with intermittent hyperglycaemia (blood glucose levels ≥7.8 mmol/L and <11.1 mmol/L). A multivariable binary logistic regression model was created to determine the association between hyperglycaemia and the need for IMV. Survival analysis was performed to assess the effect of hyperglycaemia on outcome within 30 days of hospitalization.
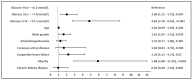
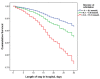
Results: Among 1945 patients without diabetes at admission, 1078 (55.4%) had normal glucose levels, 651 (33.5%) had mild hyperglycaemia, 196 (10.1%) had intermittent hyperglycaemia, and 20 (1.0%) had hypoglycaemia. The oddsratio (OR) for IMV in patients with intermittent hyperglycaemia was 4.82 (95% CI 2.70-8.61, p < 0.001), and the OR was 2.00 (95% CI 1.21-3.31, p = 0.007) in those with mild hyperglycaemia compared to patients presenting normal glucose levels. The hazardratio (HR) for 30-day in-hospital mortality in patients with mild hyperglycaemia was 1.62 (95% CI 1.10-2.39, p = 0.015), while the HR was 3.04 (95% CI 2.01-4.60, p < 0.001) in patients with intermittent hyperglycaemia compared to those with normoglycaemia at admission.
Conclusions: In COVID-19 patients without pre-existing diabetes, the presence of hyperglycaemia at admission is indicative of COVID-19-induced alterations in glucose metabolism and stress hyperglycaemia. Hyperglycaemia at admission in COVID-19 patients without diabetes is associated with an increased risk of invasive mechanical ventilation and in-hospital mortality. This finding highlights the importance for clinicians to carefully consider and select optimal support and treatment strategies for these patients. Further studies on the long-term consequences of hyperglycaemia in this specific population are warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; glucose on admission; hyperglycaemia; in-hospital mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Newly diagnosed diabetes is associated with a higher risk of mortality than known diabetes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Oct;22(10):1897-1906. doi: 10.1111/dom.14099. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 32469464 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and predictors for in-hospital mortality in adult COVID-19 patients: A retrospective single center cohort study in Vilnius, Lithuania.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0290656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290656. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37624796 Free PMC article.
-
Admission hyperglycaemia as a predictor of mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 regardless of diabetes status: data from the Spanish SEMI-COVID-19 Registry.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):103-116. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1836566. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 33063540 Free PMC article.
-
Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with intermediate hyperglycaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 29;10(10):CD012661. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012661.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30371961 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in a country with a very high prevalence of diabetes: The impact of admission hyperglycaemia on mortality.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2021 Jun 14;4(3):e00279. doi: 10.1002/edm2.279. eCollection 2021 Jul. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2021. PMID: 34277995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Stress Hyperglycemia in a Cohort of Brazilian Patients With COVID-19.Am J Med Open. 2025 May 9;14:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.ajmo.2025.100101. eCollection 2025 Dec. Am J Med Open. 2025. PMID: 40546248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plummer M.P., Bellomo R., Cousins C.E., Annink C.E., Sundararajan K., Reddi B.A., Raj J.P., Chapman M.J., Horowitz M., Deane A.M. Dysglycaemia in the critically ill and the interaction of chronic and acute glycaemia with mortality. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:973–980. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3287-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

