Involvement of Lysophospholipids in Pulmonary Vascular Functions and Diseases
- PMID: 38255229
- PMCID: PMC10813361
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12010124
Involvement of Lysophospholipids in Pulmonary Vascular Functions and Diseases
Abstract
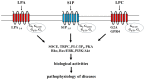
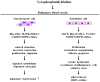
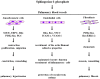
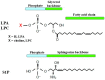
Extracellular lysophospholipids (lysophosphatidic acid, lysophosphatidylcholine, sphingosine 1-phosphate, etc.), which are synthesized from phospholipids in the cell membrane, act as lipid mediators, and mediate various cellular responses in constituent cells in the respiratory system, such as contraction, proliferation, migration, and cytoskeletal organization. In addition to these effects, the expression of the adhesion molecules is enhanced by these extracellular lysophospholipids in pulmonary endothelial cells. These effects are exerted via specific G protein-coupled receptors. Rho, Ras, and phospholipase C (PLC) have been proven to be their signaling pathways, related to Ca2+ signaling due to Ca2+ dynamics and Ca2+ sensitization. Therefore, lysophospholipids probably induce pulmonary vascular remodeling through phenotype changes in smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, likely resulting in acute respiratory distress syndrome due to vascular leak, pulmonary hypertension, and pulmonary fibrosis. Moreover, lysophospholipids induce the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the lungs via the enhancement of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells, potentially leading to the development of asthma. These results demonstrate that lysophospholipids may be novel therapeutic targets not only for injury, fibrosis, and hypertension in the lung, but also for asthma. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms of the effects of lysophospholipids on the respiratory system, and the possibility of precision medicine targeting lysophospholipids as treatable traits of these diseases.
Keywords: ARDS; asthma; lysophosphadidylcholine; lysophosphatidic acid; pulmonary endothelial cells; pulmonary fibroblasts; pulmonary fibrosis; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular smooth muscle; sphingosine 1-phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nikitopoulou I., Fanidis D., Ntatsoulis K., Moulos P., Mpekoulis G., Evangelidou M., Vassiliou A.G., Dimakopoulou V., Jahaj E., Tsipilis S., et al. Increased Autotaxin Levels in Severe COVID-19, Correlating with IL-6 Levels, Endothelial Dysfunction Biomarkers, and Impaired Functions of Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:10006. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

