Inflammatory and Hematologic Liver and Platelet (HALP) Scores in Hypothermia-Treated Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
- PMID: 38255385
- PMCID: PMC10814453
- DOI: 10.3390/children11010072
Inflammatory and Hematologic Liver and Platelet (HALP) Scores in Hypothermia-Treated Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Abstract
Objective: This study examined systemic inflammatory indices and "Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, Platelet (HALP) scores" in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
Methods: A total of 43 neonates with moderate-to-severe HIE at 36 weeks' gestation were assessed. Systemic inflammatory markers were measured before HT commenced within 0-6 h after birth and between 60 and 72 h during and after therapy or before adjusting for hypothermia.
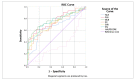
Results: Platelet counts, hemoglobin levels, and platelet indices in the HIE group were significantly lower at both time points (p = 0.001). Both the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) decreased in the HIE group after hypothermia therapy (p = 0.001). Seizures, PVL, and kidney injuries were associated with higher HALP scores. The AUCs of NLR, PLR, MLR, SII, SIRI, and platelet, neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte Index (PIV) showed significant sensitivity and specified HIE, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.654, 0.751, 0.766, 0.700, 0.722, and 0.749, respectively.
Conclusions: A significant difference in systemic inflammatory markers was found between the HIE and control groups after hypothermia treatment, with significant reductions in the MLR and NLR. These markers, particularly MLR, were significant predictors of adverse clinical outcomes including seizures, PVL, and kidney damage.
Keywords: HALP score; hypothermia therapy; hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy; neonatal care; systemic inflammatory indices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- DeLaGarza-Pineda O., Mailo J.A., Boylan G., Chau V., Glass H.C., Mathur A.M., Shellhaas R.A., Soul J.S., Wusthoff C.J., Chang T., et al., editors. Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. Management of seizures in neonates with neonatal encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. - PubMed
-
- Kariholu U., Montaldo P., Markati T., Lally P.J., Pryce R., Teiserskas J., Liow N., Oliveira V., Soe A., Shankaran S., et al. Therapeutic hypothermia for mild neonatal encephalopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020;105:225–228. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2018-315711. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abate B.B., Bimerew M., Gebremichael B., Mengesha Kassie A., Kassaw M., Gebremeskel T., Alebachew Bayih W. Effects of therapeutic hypothermia on death among asphyxiated neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0247229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources