Comparative Effects on Using Bilberry Leaves in Broiler Diet Reared under Thermoneutral Conditions vs. Heat Stress on Performance, Health Status and Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 38255654
- PMCID: PMC10821394
- DOI: 10.3390/life14010039
Comparative Effects on Using Bilberry Leaves in Broiler Diet Reared under Thermoneutral Conditions vs. Heat Stress on Performance, Health Status and Gut Microbiota
Abstract
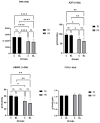
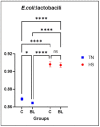
The study aims to investigate the impact of dietary bilberry leaves on the performance, health status, and gut microbiota of broilers reared in both thermoneutral conditions and under heat stress. Sixty Cobb 500 broiler chicks were divided into two groups (C-TN, BL-TN) and reared in thermoneutral conditions for the first trial. For the second trial, two other groups (C-HS and BL-HS) were reared in heat stress (32 °C), with 30 chickens in each group. The experimental diets were supplemented with 1% bilberry leaves compared to the control diets. The broilers fed a diet with bilberry leaves had lower levels of cholesterol compared to the control birds. At the end of the experiment, six broilers per group were slaughtered, and intestinal contents were collected for bacteriological analyses. The results revealed that bilberry leaves increased body weight and average daily feed intake in the BL-TN group compared to the C-HS group. However, the broilers fed a bilberry leaves diet and reared in heat stress had a significantly lower average daily feed intake and average daily weight gain than the C-TN group. Additionally, the number of staphylococci colonies decreased significantly in the group fed with a BL-supplemented diet and reared in TN compared to C-TN, while lactobacilli increased significantly in BL-TN compared to C-TN. In summary, bilberry leaves can be used as a natural supplement in a broiler's diet to regulate serum cholesterol in heat stress and maintain the health of intestinal microflora in thermoneutral conditions.
Keywords: bilberry leaves; broiler; heat stress; intestinal microflora; thermoneutral condition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary supplemental lysophospholipids and vitamin C on performance, antioxidant enzymes, lipid peroxidation, thyroid hormones and serum metabolites of broiler chickens reared under thermoneutral and high ambient temperature.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018 Dec;102(6):1521-1532. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12935. Epub 2018 Sep 25. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30255521
-
Alleviation of chronic heat stress in broilers by dietary supplementation of betaine and turmeric rhizome powder: dynamics of performance, leukocyte profile, humoral immunity, and antioxidant status.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016 Jan;48(1):181-8. doi: 10.1007/s11250-015-0941-1. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2016. PMID: 26494545 Clinical Trial.
-
Growth, immune, antioxidant, and bone responses of heat stress-exposed broilers fed diets supplemented with tomato pomace.Int J Biometeorol. 2016 Aug;60(8):1183-92. doi: 10.1007/s00484-015-1112-9. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Int J Biometeorol. 2016. PMID: 26589827
-
Low-Protein Diets Differentially Regulate Energy Balance during Thermoneutral and Heat Stress in Cobb Broiler Chicken (Gallus domesticus).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 15;25(8):4369. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084369. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673954 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of individual or combination of dietary betaine and glycine on productive performance, stress response, liver health, and intestinal barrier function in broiler chickens raised under heat stress conditions.Poult Sci. 2023 Jul;102(7):102771. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102771. Epub 2023 May 2. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37236038 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chlorella vulgaris as a Nutraceutical Source for Broilers: Improving Meat Quality and Storage Oxidative Status.Foods. 2024 Jul 27;13(15):2373. doi: 10.3390/foods13152373. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123564 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa L.) Fruit, Leaves, and Pomace for Their Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant Potential, and Polyphenol Bioaccessibility.Foods. 2024 Jun 13;13(12):1856. doi: 10.3390/foods13121856. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirakawa R., Nurjanah S., Furukawa K., Murai A., Kikusato M., Nochi T., Toyomizu M. Heat stress causes immune abnormalities via massive damage to effect proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020;7:46. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ștefănescu B.-E., Călinoiu L.F., Ranga F., Fetea F., Mocan A., Vodnar D.C., Crișan G. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of the Nord-West Romanian Wild Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) and Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) Leaves. Antioxidants. 2020;9:495. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060495. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanoeva J.P., Stefova M., Andonovska K.B., Vankov A., Stafilov T. Phenolics and mineral content in bilberry and bog bilberry from Macedonia. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017;20:S863–S883. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1315592. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

