Evolution of Consciousness
- PMID: 38255663
- PMCID: PMC10817314
- DOI: 10.3390/life14010048
Evolution of Consciousness
Abstract
The natural evolution of consciousness in different animal species mandates that conscious experiences are causally potent in order to confer any advantage in the struggle for survival. Any endeavor to construct a physical theory of consciousness based on emergence within the framework of classical physics, however, leads to causally impotent conscious experiences in direct contradiction to evolutionary theory since epiphenomenal consciousness cannot evolve through natural selection. Here, we review recent theoretical advances in describing sentience and free will as fundamental aspects of reality granted by quantum physical laws. Modern quantum information theory considers quantum states as a physical resource that endows quantum systems with the capacity to perform physical tasks that are classically impossible. Reductive identification of conscious experiences with the quantum information comprised in quantum brain states allows for causally potent consciousness that is capable of performing genuine choices for future courses of physical action. The consequent evolution of brain cortical networks contributes to increased computational power, memory capacity, and cognitive intelligence of the living organisms.
Keywords: brain cortex; causal potency; conscious experience; quantum physics; sentience.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
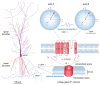





References
-
- Georgiev D.D. Quantum Information and Consciousness: A Gentle Introduction. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2017. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

