Neurosarcoidosis: The Presentation, Diagnosis and Treatment Review of Two Cases
- PMID: 38255684
- PMCID: PMC10820900
- DOI: 10.3390/life14010069
Neurosarcoidosis: The Presentation, Diagnosis and Treatment Review of Two Cases
Abstract
Sarcoidosis is a chronic granulomatous disease of unknown cause characterized by the presence of non-caseating granulomas. The disease can affect any organ including the nervous system. Neurosarcoidosis occurs in about 5% patients with sarcoidosis. The clinical presentation of neurosarcoidosis is varied, and it can involve the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system, separately or in different combinations. The diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis is challenging, as biopsies from the nervous system are not readily available. Anti-TNFα agents are becoming one of the cornerstone treatments for neurosarcoidosis. In this case-based review, we discuss two cases of neurosarcoidosis with different clinical presentations. The first patient presented with confusion, while the second presented with walking difficulty and neurogenic bladder. Both patients were treated with methylprednisolone pulse therapy with rapid, but non-complete, improvement. Therefore, infliximab was initiated in both cases with subsequent improvement in the clinical manifestations and imaging findings, emphasizing the effectiveness and safety of infliximab in cases of severe neurosarcoidosis. In conclusion, the goal of neurosarcoidosis management is to prevent organ system damage and minimize the toxic cumulative adverse effects of glucocorticoid use. In this case-based review we discuss the various presentations, the diagnosis and the treatment of neurosarcoidosis.
Keywords: anti-TNFα agents; effectiveness; infliximab; nervous system; neurosarcoidosis; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
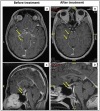
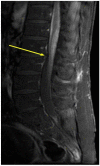
References
-
- Baughman R.P., Teirstein A.S., Judson M.A., Rossman M.D., Yeager H., Jr., Bresnitz E.A., De Palo L., Hunninghake G., Iannuzzi M.C., Johns C.J., et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001;164:1885–1889. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104046. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pietinalho A., Ohmichi M., Hiraga Y., Löfroos A.B., Selroos O. The mode of presentation of sarcoidosis in Finland and Hokkaido, Japan. A comparative analysis of 571 Finnish and 686 Japanese patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1996;13:159–166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

