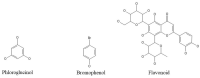
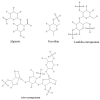
From Ocean to Medicine: Harnessing Seaweed's Potential for Drug Development
- PMID: 38255871
- PMCID: PMC10815561
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25020797
From Ocean to Medicine: Harnessing Seaweed's Potential for Drug Development
Abstract
Seaweed, a miscellaneous group of marine algae, has long been recognized for its rich nutritional composition and bioactive compounds, being considered nutraceutical ingredient. This revision delves into the promising role of seaweed-derived nutrients as a beneficial resource for drug discovery and innovative product development. Seaweeds are abundant sources of essential vitamins, minerals, polysaccharides, polyphenols, and unique secondary metabolites, which reveal a wide range of biological activities. These bioactive compounds possess potential therapeutic properties, making them intriguing candidates for drug leads in various medical applications and pharmaceutical drug development. It explores their pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities, shedding light on their potential as therapeutic agents. Moreover, the manuscript provides insights into the development of formulation strategies and delivery systems to enhance the bioavailability and stability of seaweed-derived compounds. The manuscript also discusses the challenges and opportunities associated with the integration of seaweed-based nutrients into the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. Regulatory considerations, sustainability, and scalability of sustainable seaweed sourcing and cultivation methods are addressed, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach in harnessing seaweed's potential. This revision underscores the immense potential of seaweed-derived compounds as a valuable reservoir for drug leads and product development. By bridging the gap between marine biology, pharmacology, and product formulation, this research contributes to the critical advancement of sustainable and innovative solutions in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; drug development; drug discovery; formulation strategies; pharmacological activities; seaweed-derived compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- García-Poza S., Leandro A., Cotas J., Pacheco D., Marques J.C., Pereira L., Gonçalves A.M.M. Algal Metabolites. Apple Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2023. Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Potential of Seaweed Sustainable Exploitation; pp. 287–338.
-
- Cotas J., Pacheco D., Gonçalves A.M.M., Silva P., Carvalho L.G., Pereira L. Seaweeds’ Nutraceutical and Biomedical Potential in Cancer Therapy: A Concise Review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2021;7:13. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2020.134. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous