Modulation of miR-29a and miR-29b Expression and Their Target Genes Related to Inflammation and Renal Fibrosis by an Oral Nutritional Supplement with Probiotics in Malnourished Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 38256206
- PMCID: PMC10816158
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25021132
Modulation of miR-29a and miR-29b Expression and Their Target Genes Related to Inflammation and Renal Fibrosis by an Oral Nutritional Supplement with Probiotics in Malnourished Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
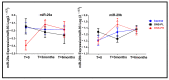
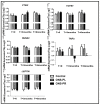
Malnutrition is prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially those on hemodialysis. Recently, our group described that a new oral nutritional supplement (ONS), specifically designed for malnourished (or at risk) hemodialysis patients with a "similar to the Mediterranean diet" pattern, improved caloric-protein intake, nutritional status and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidation. Our aim in this study was to evaluate whether the new ONS, associated with probiotics or not, may produce changes in miRNA's expression and its target genes in malnourished hemodialysis patients, compared to individualized diet recommendations. We performed a randomized, multicenter, parallel-group trial in malnourished hemodialysis patients with three groups (1: control (C) individualized diet (n = 11); 2: oral nutritional supplement (ONS) + placebo (ONS-PL) (n = 10); and 3: ONS + probiotics (ONS-PR) (n = 10)); the trial was open regarding the intake of ONS or individualized diet recommendations but double-blinded for the intake of probiotics. MiRNAs and gene expression levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR at baseline and after 3 and 6 months. We observed that the expression of miR-29a and miR-29b increased significantly in patients with ONS-PR at 3 months in comparison with baseline, stabilizing at the sixth month. Moreover, we observed differences between studied groups, where miR-29b expression levels were elevated in patients receiving ONS-PR compared to the control group in the third month. Regarding the gene expression levels, we observed a decrease in the ONS-PR group compared to the control group in the third month for RUNX2 and TNFα. TGFB1 expression was decreased in the ONS-PR group compared to baseline in the third month. PTEN gene expression was significantly elevated in the ONS-PR group at 3 months in comparison with baseline. LEPTIN expression was significantly increased in the ONS-PL group at the 3-month intervention compared to baseline. The new oral nutritional supplement associated with probiotics increases the expression levels of miR-29a and miR-29b after 3 months of intervention, modifying the expression of target genes with anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic actions. This study highlights the potential benefit of this oral nutritional supplement, especially associated with probiotics, in malnourished patients with chronic renal disease on hemodialysis.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; circulating miRNAs; gene expression; hemodialysis; inflammation; malnutrition; oral nutritional supplement; probiotics; renal fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
F.H. received honoraria support for a presentation from Adventia Pharma. G.O. received occasional honoraria support for presentations, attending meetings and travel from Adventia Pharma. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect on nutritional status and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidation of an oral nutritional supplement (with or without probiotics) in malnourished hemodialysis patients. A multicenter randomized clinical trial "Renacare Trial".Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 3;10:1107869. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1107869. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36819685 Free PMC article.
-
Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 12;17(4):652. doi: 10.3390/nu17040652. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40004979 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intradialytic oral nutrition effects on malnourished hemodialysis patients: a randomized trial.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 13;14(1):21400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72402-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39271736 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral protein-based supplements versus placebo or no treatment for people with chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 11;5(5):CD012616. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012616.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32390133 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oral nutritional supplement in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2024 Mar;13(2):260-272. doi: 10.21037/apm-23-558. Ann Palliat Med. 2024. PMID: 38584474
Cited by
-
Leptin Is Associated with Testosterone, Nutritional Markers, and Vascular Muscular Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7646. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147646. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062887 Free PMC article.
-
What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 11;26(14):6662. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146662. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic Functions in Fermented Foods: Anti-Viral, Immunomodulatory, and Anti-Cancer Benefits.Foods. 2024 Jul 28;13(15):2386. doi: 10.3390/foods13152386. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ikizler T.A., Burrowes J.D., Byham-Gray L.D., Campbell K.L., Carrero J.J., Chan W., Fouque D., Friedman A.N., Ghaddar S., Goldstein-Fuchs D.J., et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020;76:S1–S107. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hevilla F., Padial M., Blanca M., Barril G., Jiménez-Salcedo T., Ramirez-Ortiz M., Nogueira Á., Gentile A., García-Escobar E., Romero-Zerbo S.Y., et al. Effect on Nutritional Status and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation of an Oral Nutritional Supplement (with or without Probiotics) in Malnourished Hemodialysis Patients. A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial “Renacare Trial”. Front. Nutr. 2023;10:1107869. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1107869. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mompeón A., Ortega-Paz L., Vidal-Gómez X., Costa T.J., Pérez-Cremades D., Garcia-Blas S., Brugaletta S., Sanchis J., Sabate M., Novella S., et al. Disparate MiRNA Expression in Serum and Plasma of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic and Paired Comparative Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:5373. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61507-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

