MicroRNA Targets PAP1 to Mediate Melanization in Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus) Infected by Metarhizium anisopliae
- PMID: 38256210
- PMCID: PMC10816858
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25021140
MicroRNA Targets PAP1 to Mediate Melanization in Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus) Infected by Metarhizium anisopliae
Abstract
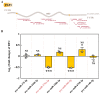
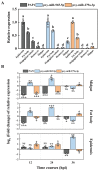
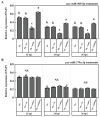
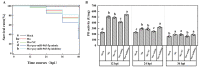
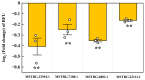
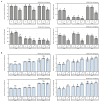
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role in important biological processes by regulating post-transcriptional gene expression and exhibit differential expression patterns during development, immune responses, and stress challenges. The diamondback moth causes significant economic damage to crops worldwide. Despite substantial advancements in understanding the molecular biology of this pest, our knowledge regarding the role of miRNAs in regulating key immunity-related genes remains limited. In this study, we leveraged whole transcriptome resequencing data from Plutella xylostella infected with Metarhizium anisopliae to identify specific miRNAs targeting the prophenoloxidase-activating protease1 (PAP1) gene and regulate phenoloxidase (PO) cascade during melanization. Seven miRNAs (pxy-miR-375-5p, pxy-miR-4448-3p, pxy-miR-279a-3p, pxy-miR-3286-3p, pxy-miR-965-5p, pxy-miR-8799-3p, and pxy-miR-14b-5p) were screened. Luciferase reporter assays confirmed that pxy-miR-279a-3p binds to the open reading frame (ORF) and pxy-miR-965-5p to the 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) of PAP1. Our experiments demonstrated that a pxy-miR-965-5p mimic significantly reduced PAP1 expression in P. xylostella larvae, suppressed PO activity, and increased larval mortality rate. Conversely, the injection of pxy-miR-965-5p inhibitor could increase PAP1 expression and PO activity while decreasing larval mortality rate. Furthermore, we identified four LncRNAs (MSTRG.32910.1, MSTRG.7100.1, MSTRG.6802.1, and MSTRG.22113.1) that potentially interact with pxy-miR-965-5p. Interference assays using antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) revealed that silencing MSTRG.7100.1 and MSTRG.22113.1 increased the expression of pxy-miR-965-5p. These findings shed light on the potential role of pxy-miR-965-5p in the immune response of P. xylostella to M. anisopliae infection and provide a theoretical basis for biological control strategies targeting the immune system of this pest.
Keywords: diamondback moth; melanization; non-coding RNAs; pest management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of microRNA miR-2b-3p in regulation of metabolic resistance to insecticides in Plutella xylostella.Insect Mol Biol. 2018 Aug;27(4):478-491. doi: 10.1111/imb.12387. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Insect Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29573306
-
Spatio-Temporal Profiling of Metarhizium anisopliae-Responsive microRNAs Involved in Modulation of Plutella xylostella Immunity and Development.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;7(11):942. doi: 10.3390/jof7110942. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829229 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of developmental features in the immune system of Plutella xylostella during larva-to-adult metamorphosis.Genomics. 2022 Jul;114(4):110381. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110381. Epub 2022 May 6. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35533967
-
miR-140-5p and miR-140-3p: Key Actors in Aging-Related Diseases?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 28;23(19):11439. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911439. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of microRNAs from Plutella xylostella larvae associated with parasitization by Diadegma semiclausum.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;43(4):309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23352895 Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental Expression Patterns of miRNA in Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidotera: Noctuidae).Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;16(2):234. doi: 10.3390/genes16020234. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004562 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

