Salivary Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38256241
- PMCID: PMC10817083
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25021168
Salivary Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
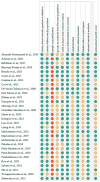
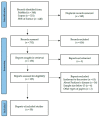
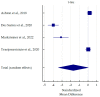
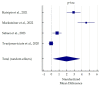
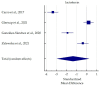
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease which manifests with progressive cognitive impairment, leading to dementia. Considering the noninvasive collection of saliva, we designed the systematic review to answer the question "Are salivary biomarkers reliable for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease?" Following the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 30 studies were included in this systematic review (according to the PRISMA statement guidelines). Potential biomarkers include mainly proteins, metabolites and even miRNAs. Based on meta-analysis, in AD patients, salivary levels of beta-amyloid42 and p-tau levels were significantly increased, and t-tau and lactoferrin were decreased at borderline statistical significance. However, according to pooled AUC, lactoferrin and beta-amyloid42 showed a significant predictive value for salivary-based AD diagnosis. In conclusion, potential markers such as beta-amyloid42, tau and lactoferrin can be detected in the saliva of AD patients, which could reliably support the early diagnosis of this neurodegenerative disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease; beta-amyloid; biomarkers; lactoferrin; neurodegenerative diseases; saliva; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Aβ1-42 may be a quick-tested biomarker for clinical use in Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2023 Apr;270(4):1945-1954. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11509-w. Epub 2022 Dec 23. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36562850 Review.
-
CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Neurol. 2016 Jun;15(7):673-684. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00070-3. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Lancet Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27068280
-
Salivary Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Cells. 2024 Feb 14;13(4):340. doi: 10.3390/cells13040340. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391952 Free PMC article.
-
¹⁸F-FDG PET for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 28;1(1):CD010632. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010632.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25629415 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Wearable Healthcare Devices: From Material to Application.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Apr 6;11(4):358. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11040358. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: Emerging trends and clinical implications.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 May 5;138(9):1009-1012. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003579. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40169365 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The neuroinflammatory role of microglia in Alzheimer's disease and their associated therapeutic targets.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jul;30(7):e14856. doi: 10.1111/cns.14856. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39031970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Oral Biomarkers in the Assessment of Noncommunicable Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;15(1):78. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010078. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Plasma Lactoferrin Concentrations Between Subjects with Normal Cognitive Function and Mild Cognitive Impairment: An Observational Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;13(8):872. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080872. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281821 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

