Radiomic Analysis in Pituitary Tumors: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 38256471
- PMCID: PMC10816809
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13020336
Radiomic Analysis in Pituitary Tumors: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives
Abstract
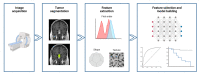
Radiomic analysis has emerged as a valuable tool for extracting quantitative features from medical imaging data, providing in-depth insights into various contexts and diseases. By employing methods derived from advanced computational techniques, radiomics quantifies textural information through the evaluation of the spatial distribution of signal intensities and inter-voxel relationships. In recent years, these techniques have gained considerable attention also in the field of pituitary tumors, with promising results. Indeed, the extraction of radiomic features from pituitary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images has been shown to provide useful information on various relevant aspects of these diseases. Some of the key topics that have been explored in the existing literature include the association of radiomic parameters with histopathological and clinical data and their correlation with tumor invasiveness and aggressive behavior. Their prognostic value has also been evaluated, assessing their role in the prediction of post-surgical recurrence, response to medical treatments, and long-term outcomes. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge and application of radiomics in pituitary tumors. It also examines the current limitations and future directions of radiomic analysis, highlighting the major challenges that need to be addressed before a consistent integration of these techniques into routine clinical practice.
Keywords: PitNET; consistency; histology; invasiveness; pituitary adenoma; pituitary tumor; radiomics; recurrence; treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Raverot G., Burman P., McCormack A., Heaney A., Petersenn S., Popovic V., Trouillas J., Dekkers O.M. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of aggressive pituitary tumours and carcinomas. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018;178:G1–G24. doi: 10.1530/EJE-17-0796. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources