Quantification of hs-Troponin Levels and Global Longitudinal Strain among Critical COVID-19 Patients with Myocardial Involvement
- PMID: 38256486
- PMCID: PMC10816186
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13020352
Quantification of hs-Troponin Levels and Global Longitudinal Strain among Critical COVID-19 Patients with Myocardial Involvement
Abstract
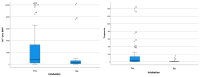
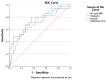
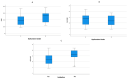
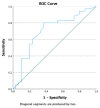
Background. Myocardial involvement among critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) often has worse outcomes. An imbalance in the oxygen supply causes the excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which results in increased ventilation requirements and the risk of death in COVID-19 patients. Purpose. We evaluated the association between the hs-troponin I levels and global longitudinal strain (GLS) as evidence of myocardial involvement among critical COVID-19 patients. Methods. We conducted a prospective cohort study from 1 February to 31 July 2021 at RSUD Dr. Soetomo, Surabaya, as a COVID-19 referral center. Of the 65 critical COVID-19 patients included, 41 (63.1%) were men, with a median age (interquartile range) of 51.0 years (20.0-75.0). Subjects were recruited based on WHO criteria for severe COVID-19, and myocardial involvement in the form of myocarditis was assessed using CDC criteria. Subjects were examined using echocardiography to measure the GLS, and blood samples were taken to measure the hs-troponin. Subjects were then followed for their need for mechanical ventilation and in-hospital mortality. Results. Severe COVID-19 patients with cardiac injury were associated with an increased need for intubation (78.5%) and an increased incidence of myocarditis (50.8%). There was a relationship between the use of intubation and the risk of death in patients (66.7% vs. 33.3%, p-value < 0.001). Decreased GLS and increased hs-troponin were associated with increased myocarditis (p values < 0.001 and 0.004, respectively). Decreased GLS was associated with a higher need for mechanical ventilation (12.17 + 4.79 vs. 15.65 + 4.90, p-value = 0.02) and higher mortality (11.36 + 4.64 vs. 14.74 + 4.82; p-value = 0.005). Elevated hs-troponin was associated with a higher need for mechanical ventilation (25.33% vs. 3.56%, p-value = 0.002) and higher mortality (34.57% vs. 5.76%, p-value = 0.002). Conclusions. Critically ill COVID-19 patients with myocardial involvement and elevated cardiac troponin levels are associated with a higher need for mechanical ventilation and higher mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19; global longitudinal strain; hs-troponin; mechanical ventilation; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kemenkes R.I. Situasi Terkini COVID19. 2020. [(accessed on 1 June 2020)]. Internet. Available online: https://covid19.kemkes.go.id/situasi-infeksi-emerging/situasi-terkini-pe....
-
- Chen C., Yan J.T., Zhou N., Zhao J.P., Wang D.W. Analysis of myocardial injury in patients with COVID-19 and association between concomitant cardiovascular diseases and severity of COVID-19. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020;48:e008. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

