Cytocompatibility, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of a Mucoadhesive Biopolymeric Hydrogel Embedding Selenium Nanoparticles Phytosynthesized by Sea Buckthorn Leaf Extract
- PMID: 38256857
- PMCID: PMC10819796
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17010023
Cytocompatibility, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of a Mucoadhesive Biopolymeric Hydrogel Embedding Selenium Nanoparticles Phytosynthesized by Sea Buckthorn Leaf Extract
Abstract
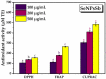
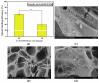
Phytosynthesized selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) are less toxic than the inorganic salts of selenium and show high antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Chitosan prevents microbial biofilm formation and can also determine microbial biofilm dispersal. Never-dried bacterial nanocellulose (NDBNC) is an efficient carrier of bioactive compounds and a flexible nanofibrillar hydrophilic biopolymer. This study aimed to develop a selenium-enriched hydrogel nanoformulation (Se-HNF) based on NDBNC from kombucha fermentation and fungal chitosan with embedded biogenic SeNPs phytosynthesized by an aqueous extract of sea buckthorn leaves (SbLEx)-SeNPsSb-in order to both disperse gingival dysbiotic biofilm and prevent its development. We determined the total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of SbLEx. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) were used for the identification of polyphenols from SbLEx. SeNPsSb were characterized by transmission electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (TEM-EDX), dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) in small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS and WAXS). The hydrogel nanoformulation with embedded SeNPsSb was characterized by SEM, FTIR, XRD, rheology, mucin binding efficiency, contact angle and interfacial tension measurements. We also assessed the in vitro biocompatibility, antioxidant activity and antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of SeNPsSb and Se-HNF. TEM, DLS and SAXS evidenced polydisperse SeNPsSb, whereas FTIR highlighted a heterogeneous biocorona with various biocompounds. The contact angle on the polar surface was smaller (52.82 ± 1.23°) than that obtained on the non-polar surface (73.85 ± 0.39°). The interfacial tension was 97.6 ± 0.47 mN/m. The mucin binding efficiency of Se-HNF decreased as the amount of hydrogel decreased, and the SEM analysis showed a relatively compact structure upon mucin contact. FTIR and XRD analyses of Se-HNF evidenced an interaction between BNC and CS through characteristic peak shifting, and the rheological measurements highlighted a pseudoplastic behavior, 0.186 N adhesion force and 0.386 adhesion energy. The results showed a high degree of cytocompatibility and the significant antioxidant and antimicrobial efficiency of SeNPsSb and Se-HNF.
Keywords: bacterial nanocellulose; fungal chitosan; gingival dysbiotic biofilm; phytosynthesized selenium nanoparticles; sea buckthorn leaf extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Bioactive Hydrogel Formulation Based on Ferulic Acid-Grafted Nano-Chitosan and Bacterial Nanocellulose Enriched with Selenium Nanoparticles from Kombucha Fermentation.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jul 22;15(7):202. doi: 10.3390/jfb15070202. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39057323 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium-Fortified Kombucha-Pollen Beverage by In Situ Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles with High Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 2;12(9):1711. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091711. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760014 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive-Loaded Hydrogels Based on Bacterial Nanocellulose, Chitosan, and Poloxamer for Rebalancing Vaginal Microbiota.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;16(12):1671. doi: 10.3390/ph16121671. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139798 Free PMC article.
-
Green and ecofriendly biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Urtica dioica (stinging nettle) leaf extract: Antimicrobial and anticancer activity.Biotechnol J. 2022 Feb;17(2):e2100432. doi: 10.1002/biot.202100432. Epub 2021 Nov 21. Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 34747563
-
Bombax ceiba flower extract mediated synthesis of Se nanoparticles for antibacterial activity and urea detection.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 17;39(3):80. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03513-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36646906
Cited by
-
Bioactive Hydrogel Formulation Based on Ferulic Acid-Grafted Nano-Chitosan and Bacterial Nanocellulose Enriched with Selenium Nanoparticles from Kombucha Fermentation.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jul 22;15(7):202. doi: 10.3390/jfb15070202. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39057323 Free PMC article.
-
Kombucha Versus Vegetal Cellulose for Affordable Mucoadhesive (nano)Formulations.Gels. 2025 Jan 4;11(1):37. doi: 10.3390/gels11010037. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39852008 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave assisted solvothermal green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using sea buckthorn for multiple myeloma and monocytic leukemia treatment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11532-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670555 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhamnetin: Reviewing Recent Developments in Anticancer Mechanisms and Nanoformulation-Driven Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 30;26(15):7381. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157381. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles from Dahlia pinnata tuberous roots with antibacterial, antidiabetic, and erythrocyte membrane protective activities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27177. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12457-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715446 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- Project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352-SECVENT, Sequential processes to close bioeconomy side stream and innovative bioproducts resulted from these, contract 81/2016, SMIS 105684, funded by subsidiary projects 1392/2022 NutriCel and 1393/2022 LactiFruct/Cohesion Funds of the European Union
- con-tract 81/2016, SMIS 105684; 1392/2022 NutriCel and 1393/2022 LactiFruct; 23.06.02.01 InteGral, Nucleu Program;/project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352-SECVENT; Cohesion Funds of the European Union;the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, project PN;
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

