Effect of Acute Caffeine Intake on Fat Oxidation Rate during Fed-State Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38257100
- PMCID: PMC10819049
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16020207
Effect of Acute Caffeine Intake on Fat Oxidation Rate during Fed-State Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
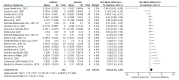
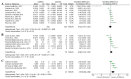
Pre-exercise intake of caffeine (from ~3 to 9 mg/kg) has been demonstrated as an effective supplementation strategy to increase fat oxidation during fasted exercise. However, a pre-exercise meal can alter the potential effect of caffeine on fat oxidation during exercise as caffeine modifies postprandial glycaemic and insulinemic responses. Hypothetically, the effect of caffeine on fat oxidation may be reduced or even withdrawn during fed-state exercise. The present systematic review aimed to meta-analyse investigations on the effect of acute caffeine intake on the rate of fat oxidation during submaximal aerobic exercise performed in the fed state (last meal < 5 h before exercise). A total of 18 crossover trials with randomised and placebo-controlled protocols and published between 1982 and 2021 were included, with a total of 228 participants (185 males and 43 females). Data were extracted to compare rates of fat oxidation during exercise with placebo and caffeine at the same exercise intensity, which reported 20 placebo-caffeine pairwise comparisons. A meta-analysis of the studies was performed, using the standardised mean difference (SMD) estimated from Hedges' g, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). In comparison with the placebo, caffeine increased the rate of fat oxidation during fed-state exercise (number of comparisons (n) = 20; p = 0.020, SMD = 0.65, 95% CI = 0.20 to 1.20). Only studies with a dose < 6 mg/kg of caffeine (n = 13) increased the rate of fat oxidation during fed-state exercise (p = 0.004, SMD = 0.86, 95% CI = 0.27 to 1.45), while no such effect was observed in studies with doses ≥6 mg/kg (n = 7; p = 0.97, SMD = -0.03, 95% CI = -1.40 to 1.35). The effect of caffeine on fat oxidation during fed-state exercise was observed in active untrained individuals (n = 13; p < 0.001, SMD = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.39 to 1.30) but not in aerobically trained participants (n = 7; p = 0.27, SMD = 0.50, 95% CI = -0.39 to 1.39). Likewise, the effect of caffeine on fat oxidation was observed in caffeine-naïve participants (n = 9; p < 0.001, SMD = 0.82, 95% CI = 0.45 to 1.19) but not in caffeine consumers (n = 3; p = 0.54, SMD = 0.57, 95% CI = -1.23 to 2.37). In conclusion, acute caffeine intake in combination with a meal ingested within 5 h before the onset of exercise increased the rate of fat oxidation during submaximal aerobic exercise. The magnitude of the effect of caffeine on fat oxidation during fed-state exercise may be modulated by the dose of caffeine administered (higher with <6 mg/kg than with ≥6 mg/kg), participants' aerobic fitness level (higher in active than in aerobically trained individuals), and habituation to caffeine (higher in caffeine-naïve than in caffeine consumers).
Keywords: aerobic exercise; breakfast; fat metabolism; stimulant; supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Caffeine Intake on Endurance Running Performance and Time to Exhaustion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 28;15(1):148. doi: 10.3390/nu15010148. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615805 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplementation for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD000998. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000998.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235577 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Coffee's Impact on Health and Well-Being.Nutrients. 2025 Aug 5;17(15):2558. doi: 10.3390/nu17152558. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Caffeine on Exercise in Hot Environments: A Bibliometric Study.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 30;16(21):3692. doi: 10.3390/nu16213692. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing Matters: Time of Day Impacts the Ergogenic Effects of Caffeine-A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 May 8;16(10):1421. doi: 10.3390/nu16101421. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38794659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guest N.S., VanDusseldorp T.A., Nelson M.T., Grgic J., Schoenfeld B.J., Jenkins N.D.M., Arent S.M., Antonio J., Stout J.R., Trexler E.T., et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Caffeine and Exercise Performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021;18:1–37. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00383-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

