Flaxseed Lignan Alleviates the Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity Associated with Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolome
- PMID: 38257189
- PMCID: PMC10821007
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16020295
Flaxseed Lignan Alleviates the Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity Associated with Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolome
Abstract
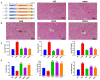
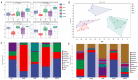
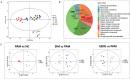
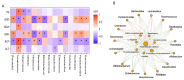
This study examined the protective effect of flaxseed lignans on liver damage caused by an overdose of paracetamol (PAM). The findings demonstrated that administering 800 mg/kg/d flaxseed lignan prior to PAM significantly decreased the serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and total bilirubin (TBi) levels, while it increased liver superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) levels in mice. Flaxseed lignan renovated the gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by PAM by promoting the proliferation of sulfonolipid (SL) producing bacteria such as Alistipes and lignan-deglycosolating bacteria such as Ruminococcus while inhibiting the growth of opportunistic pathogen bacteria such as Acinetobacter and Clostridium. Furthermore, flaxseed lignan modulated the serum metabolomic profile after PAM administration, specifically in the taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, and pyrimidine metabolism. The study identified eight potential biomarkers, including enterolactone, cervonyl carnitine, acutilobin, and PC (20:3(5Z, 8Z, 11Z)/20:0). Overall, the results suggest that flaxseed lignan can alleviate PAM-induced hepatotoxicity and may be beneficial in preventing drug-induced microbiome and metabolomic disorders.
Keywords: flaxseed lignan; gut microbiota; liver injury; paracetamol; untargeted metabolome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Christensenella minuta Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Regulating Phenylalanine Metabolism.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 18;16(14):2314. doi: 10.3390/nu16142314. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064757 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic effect of flaxseed oil against radiation-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.Phytother Res. 2007 Sep;21(9):852-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2169. Phytother Res. 2007. PMID: 17486687
-
Protective effect of a lignan-containing flaxseed extract against CCl(4)-induced hepatic injury.J Vet Med Sci. 2002 Sep;64(9):761-5. doi: 10.1292/jvms.64.761. J Vet Med Sci. 2002. PMID: 12399598
-
Flaxseed and its lignan and oil components: can they play a role in reducing the risk of and improving the treatment of breast cancer?Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014 Jun;39(6):663-78. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2013-0420. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014. PMID: 24869971 Review.
-
A Review of Lignan Metabolism, Milk Enterolactone Concentration, and Antioxidant Status of Dairy Cows Fed Flaxseed.Molecules. 2018 Dec 22;24(1):41. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010041. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30583523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure modification of luteolin and the influence of its derivatives on biological activities.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 12;12:1546932. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1546932. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40144571 Free PMC article.
-
S-amlodipine induces liver inflammation and dysfunction through the alteration of intestinal microbiome in a rat model.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2316923. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2316923. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38400721 Free PMC article.
-
An untargeted comparative metabolomics analysis of infants with and without late-onset breast milk jaundice.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 12;19(8):e0308710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308710. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39133689 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Insights and Cytochrome P450 Gene Analysis in Kadsura coccinea for Lignan Biosynthesis.Genes (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;15(3):270. doi: 10.3390/genes15030270. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Locigno R., Pincemail J., Henno A., Treusch G., Castronovo V. S-acetyl-glutathione selectively induces apoptosis in human lymphoma cells through a GSH-independent mechanism. Int. J. Oncol. 2002;20:69–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

