Evaluation of the Feasibility of In Vitro Metabolic Interruption of Trimethylamine with Resveratrol Butyrate Esters and Its Purified Monomers
- PMID: 38257342
- PMCID: PMC10820948
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29020429
Evaluation of the Feasibility of In Vitro Metabolic Interruption of Trimethylamine with Resveratrol Butyrate Esters and Its Purified Monomers
Abstract
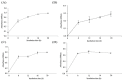
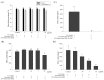
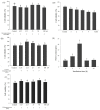
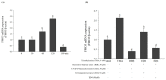
Resveratrol (RSV), obtained from dietary sources, has been shown to reduce trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) levels in humans, and much research indicates that TMAO is recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Therefore, this study investigated the effects of RSV and RSV-butyrate esters (RBE) on the proliferation of co-cultured bacteria and HepG2 cell lines, respectively, and also investigated the changes in trimethylamine (TMA) and TMOA content in the medium and flavin-containing monooxygenase-3 (FMO3) gene expression. This study revealed that 50 µg/mL of RBE could increase the population percentage of Bifidobacterium longum at a rate of 53%, while the rate was 48% for Clostridium asparagiforme. In contrast, co-cultivation of the two bacterial strains effectively reduced TMA levels from 561 ppm to 449 ppm. In addition, regarding TMA-induced HepG2 cell lines, treatment with 50 μM each of RBE, 3,4'-di-O-butanoylresveratrol (ED2), and 3-O-butanoylresveratrol (ED4) significantly reduced FMO3 gene expression from 2.13 to 0.40-1.40, which would also contribute to the reduction of TMAO content. This study demonstrated the potential of RBE, ED2, and ED4 for regulating TMA metabolism in microbial co-cultures and cell line cultures, which also suggests that the resveratrol derivative might be a daily dietary supplement that will be beneficial for health promotion in the future.
Keywords: co-cultured; metabolism; probiotic; short-chain fatty acid (SCFA); trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Purified Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Monomers against Hypertension after Maternal High-Fructose Intake in Adult Offspring.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3132. doi: 10.3390/nu16183132. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339732 Free PMC article.
-
Separation and Identification of Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Complexes and Their Bioactivity in HepG2 Cell Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13539. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413539. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948341 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of intestinal trimethylamine by probiotics ameliorated lipid metabolic disorders associated with atherosclerosis.Nutrition. 2020 Nov-Dec;79-80:110941. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110941. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Nutrition. 2020. PMID: 32858376
-
Cardiovascular risk of dietary trimethylamine oxide precursors and the therapeutic potential of resveratrol and its derivatives.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Mar;14(3):358-379. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13762. Epub 2024 Jan 21. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 38151750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trimethylamine N-Oxide: A Link among Diet, Gut Microbiota, Gene Regulation of Liver and Intestine Cholesterol Homeostasis and HDL Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 19;19(10):3228. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103228. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to choline unavailability and NAFLD development.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Jan 8;24(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01511-6. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 39801684
-
Resveratrol Propionate Ester Supplement Exerts Antihypertensive Effect in Juvenile Rats Exposed to an Adenine Diet via Gut Microbiota Modulation.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 4;16(13):2131. doi: 10.3390/nu16132131. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999878 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Sausage Simulates High Calorie-Induced Obesity In Vivo, Identifying the Potential Benefits of Weight Loss and Metabolic Syndrome of Resveratrol Butyrate Monomer Derivatives.J Nutr Metab. 2025 May 16;2025:8414627. doi: 10.1155/jnme/8414627. eCollection 2025. J Nutr Metab. 2025. PMID: 40415762 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Purified Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Monomers against Hypertension after Maternal High-Fructose Intake in Adult Offspring.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 17;16(18):3132. doi: 10.3390/nu16183132. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339732 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in research to mitigate residual risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 12;30(1):735. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-03006-3. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40796909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roncal C., Martínez-Aguilar E., Orbe J., Ravassa S., Fernandez-Montero A., Saenz-Pipaon G., Ugarte A., Estella-Hermoso de Mendoza A., Rodriguez J.A., Fernández-Alonso S., et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) Predicts Cardiovascular Mortality in Peripheral Artery Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:15580. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52082-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 112-2221-E-992 -002 -MY3/National Science and Technology Council funded this research, the Republic of China
- 111-2622-E-992-007-/National Science and Technology Council funded this research, the Republic of China
- 111-2221-E-328-001-MY3/National Science and Technology Council funded this research, the Republic of China
- 110-2320-B-992-001-MY3/National Science and Technology Council funded this research, the Republic of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

