Immunocytochemical Analysis of Crocin against Oxidative Stress in Trigeminal Sensory Neurons Innervating the Cornea
- PMID: 38257369
- PMCID: PMC10818698
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29020456
Immunocytochemical Analysis of Crocin against Oxidative Stress in Trigeminal Sensory Neurons Innervating the Cornea
Abstract
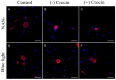
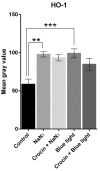
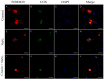
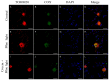
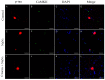
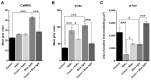
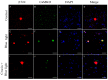
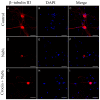
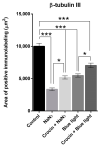
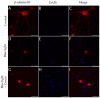
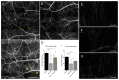
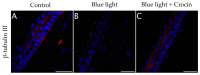
Corneal diseases are a major cause of vision loss, often associated with aging, trauma and disease. Damage to corneal sensory innervation leads to discomfort and pain. Environmental stressors, such as short-wavelength light, can induce oxidative stress that alters mitochondrial function and affects cell and tissue homeostasis, including corneal innervation. Cellular antioxidant mechanisms may attenuate oxidative stress. This study investigates crocin, a derivative of saffron, as a potential antioxidant therapy. In vitro rat trigeminal sensory ganglion neurons were exposed to both sodium azide and blue light overexposure as a model of oxidative damage. Crocin was used as a neuroprotective agent. Mitochondrial and cytoskeletal markers were studied by immunofluorescence analysis to determine oxidative damage and neuroprotection. In vivo corneal innervation degeneration was evaluated in cornea whole mount preparations using Sholl analyses. Blue light exposure induces oxidative stress that affects trigeminal neuron mitochondria and alters sensory axon dynamics in vitro, and it also affects corneal sensory innervation in an in vivo model. Our results show that crocin was effective in preserving mitochondrial function and protecting corneal sensory neurons from oxidative stress. Crocin appears to be a promising candidate for the neuroprotection of corneal innervation.
Keywords: corneal innervation; crocin; neuroprotection; saffron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crocin protects retinal ganglion cells against H2O2-induced damage through the mitochondrial pathway and activation of NF-κB.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jan;37(1):225-32. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2418. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26718031
-
Effect of short-term oral supplementation of crocin on age-related oxidative stress, cholinergic, and mitochondrial dysfunction in rat cerebral cortex.Life Sci. 2020 Dec 15;263:118545. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118545. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33038382
-
Antidepressant activity of crocin-I is associated with amelioration of neuroinflammation and attenuates oxidative damage induced by corticosterone in mice.Physiol Behav. 2019 Dec 1;212:112699. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112699. Epub 2019 Oct 12. Physiol Behav. 2019. PMID: 31614158
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in corneal disease.Mitochondrion. 2017 Sep;36:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2017.05.009. Epub 2017 May 23. Mitochondrion. 2017. PMID: 28549842 Review.
-
Therapeutic implications of crocin in Parkinson's disease: A review of preclinical research.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 Jun;101(6):1229-1240. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14210. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 36752710 Review.
References
-
- Alcalde I., Íñigo-Portugués A., González-González O., Almaraz L., Artime E., Morenilla-Palao C., Gallar J., Viana F., Merayo-Lloves J., Belmonte C. Morphological and Functional Changes in TRPM8-Expressing Corneal Cold Thermoreceptor Neurons during Aging and Their Impact on Tearing in Mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018;526:1859–1874. doi: 10.1002/cne.24454. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

